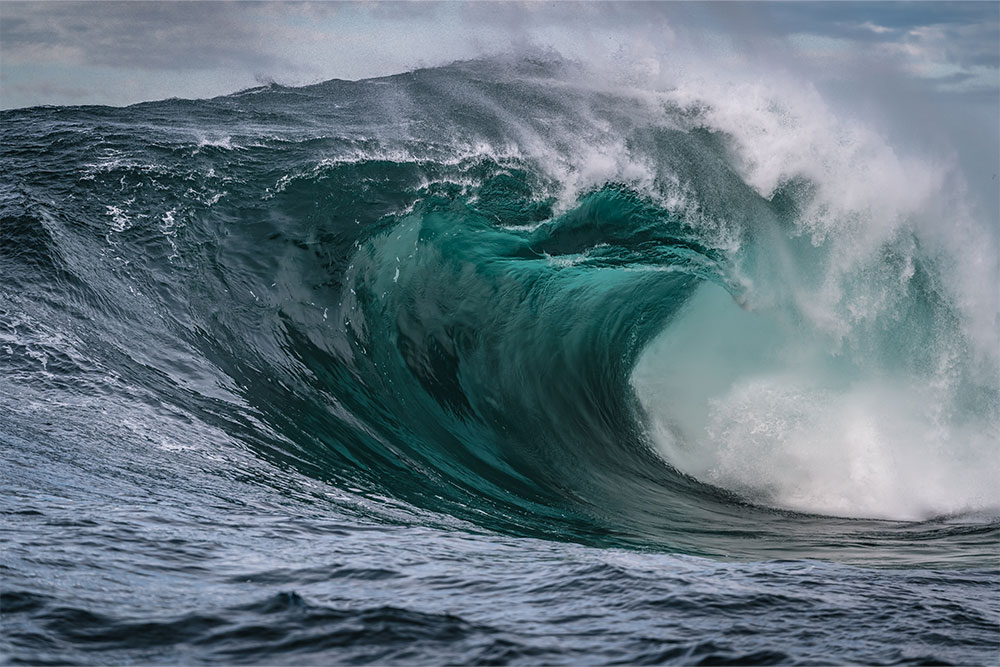
Thalassophobia is an irrational fear of the ocean or other large bodies of water. For some people, even just being shown a picture of the sea is enough to trigger feelings of dread and panic.
While being wary of deep water is not unusual, thalassophobia is more intense than concern about what’s under your boat. Sufferers can’t bear the thought of being anywhere near deep water and often experience physical symptoms like dizziness, nausea and shortness of breath.
Living with it can be difficult. But help is available and there are methods you can use to lessen its effects. In time, recovery is possible.
Read on to learn precisely what thalassophobia is, how it affects people and what to do about it.
(Please note you may find some of the following descriptions triggering. Feel free to skip over these parts and go to the advice at the end.)
What is Thalassophobia?
Back in December 1975, a movie was released in the US that went on to cause people across the world to become afraid of the ocean. That movie was Jaws, Steven Spielberg’s iconic tale about a seaside community terrorised by a great white shark. After seeing Jaws for the first time, many moviegoers developed a fear of what might be lurking under the blue waves of the ocean.
People with this phobia aren’t afraid of water but of what might be under its surface. It can also manifest as the intense fear of drowning in a deep body of water.
At first glance, the description of thalassophobia doesn’t sound entirely unreasonable. After all, humans have been telling terrifying stories about sea monsters for centuries. And more than a few creatures under the sea wouldn’t mind having us for lunch. Drowning is also a genuine risk.
If you think about it, most people aren’t comfortable being far out at sea with miles of deep blue ocean beneath them. We’re not all meant to become the next Jacques Cousteau. So why is this phobia a problem?
Where it differs from the usual wariness of the deep ocean is in how extreme it is. A sufferer has a level of fear that is entirely disproportionate to the amount of actual risk they face.
Thalassophobia is derived from two Greek words: ‘thalasso’, which means ‘sea’ and ‘phobia’, which means fear. Technically speaking, it’s a general anxiety disorder that’s listed by the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM5) as a ‘specific phobia’. It’s like fearing mice or being terrified of an injection needle at the doctor.
Getting a needle or seeing a mouse probably won’t harm you. But phobias often aren’t 100% logical.
A person may become visibly upset about going on a boat. They might experience a panic attack while sitting by a lake or on the beach. And anyone who has thalassophobia is going to find Jaws extremely disturbing and upsetting, fake mechanical shark or not.
What Are the Symptoms of Thalassophobia?
Thalassophobia is an anxiety disorder that causes, as one might guess, feelings of anxiety. No surprise there. What is surprising is how extreme these feelings can be.
Sufferers can experience intense feelings of dread and fear. They may feel as if they are in imminent danger and are at risk of dying. Their bodies go into a state of chronic stress as their ‘fight or flight’ response kicks in. Their thoughts can begin to race, panic can set in and a range of physical symptoms can occur.
A person with thalassophobia may experience strong emotional, psychological and physical reactions:
- Shortness of breath
- Excessive sweating
- Trembling
- A dry mouth
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Chest pains
- An increased heart rate
- Chills
- Nausea
- Confusion
- Light-headedness
- Tense muscles
How Common is Thalassophobia?
Phobias are more common than you may realise. Almost 52% of all adults in the UK say they have a phobia of some kind, according to research from the British government. The most common phobias are:
- Fear of spiders
- Fear of heights
- Fear of public speaking
- Fear of flying
- Fear of clowns
- Fear of mice and rats
- Fear of enclosed spaces
Unfortunately, there hasn’t been a lot of research, but some experts have estimated that up to 9% of adults have thalassophobia. Still, many more may fail to get a formal diagnosis.

Researchers do know that it often overlaps with other phobias, such as aquaphobia (the fear of water), bathophobia (the fear of depths) and megalohydrothalassophobia (the fear of large underwater creatures or objects).
What Are the Causes of Thalassophobia?
Despite the lack of specific research, we know that many factors contribute to the development of phobias.
Phobias can be caused by one or a combination of the below factors:
- Genetics: Your genetics can make you more predisposed to specific phobias. Some 67% of participants in a clinical study were found to have inherited fears at an estimated rate of 30% to 50%
- Past Experience: Having a traumatic experience, such as witnessing a near drowning or almost being drowned yourself, can cause this phobia to develop
- Dysfunctional Brain Circuitry: How your brain is wired can also cause a phobia. If your brain circuitry is dysfunctional, it can result in anxiety disorders, as one study in 2017 showed
- Family Upbringing: As well as being genetically inherited, phobias can also result from learned behaviour. If you’ve grown up in a family environment where one or more adults have had an extreme fear of the ocean, you may develop that fear yourself
How is Thalassophobia Diagnosed?
Going on the criteria listed by the DSM-5, a person is thought to have thalassophobia if:
- The person experiences intense fear or anxiety about being in, on, or near large bodies of water
- Triggers (like thoughts, images or descriptions of deep water) always lead to intense fear and anxiety
- The fear and anxiety are highly disproportionate to the actual risk of harm
- The person actively and consciously avoids triggers
- The person suffers from severe distress or impaired functioning
- The phobia is persistent and has lasted for longer than six months
- The phobia can’t be explained by other mental health conditions, such as obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
Diagnosis is a tricky business and should only be done by an experienced mental health professional.
How Is Thalassophobia Treated?
The first step is to consult with your GP. Your doctor can refer you to a mental health professional who can then make a proper diagnosis.
Some treatments can help you alleviate the symptoms and eventually overcome your phobia. These aren’t specifically for this phobia but are successfully used to treat phobias in general:
- Cognitive-Behaviour Therapy (CBT): CBT is a technique where a professional therapist has sessions with a person to help them understand and challenge their anxious thoughts.
- Exposure Therapy: This technique involves gradually exposing the person to the thing or situation they fear. A trained therapist must do this treatment in a safe, controlled environment.
- Medication: In some cases, a mental health professional may recommend a course of medication to help a person deal with the severe effects of a phobia.
- Relaxation Techniques: Many people find that relaxation techniques can lessen their anxiety. Relaxation techniques can include meditation, breathing exercises or distraction exercises.
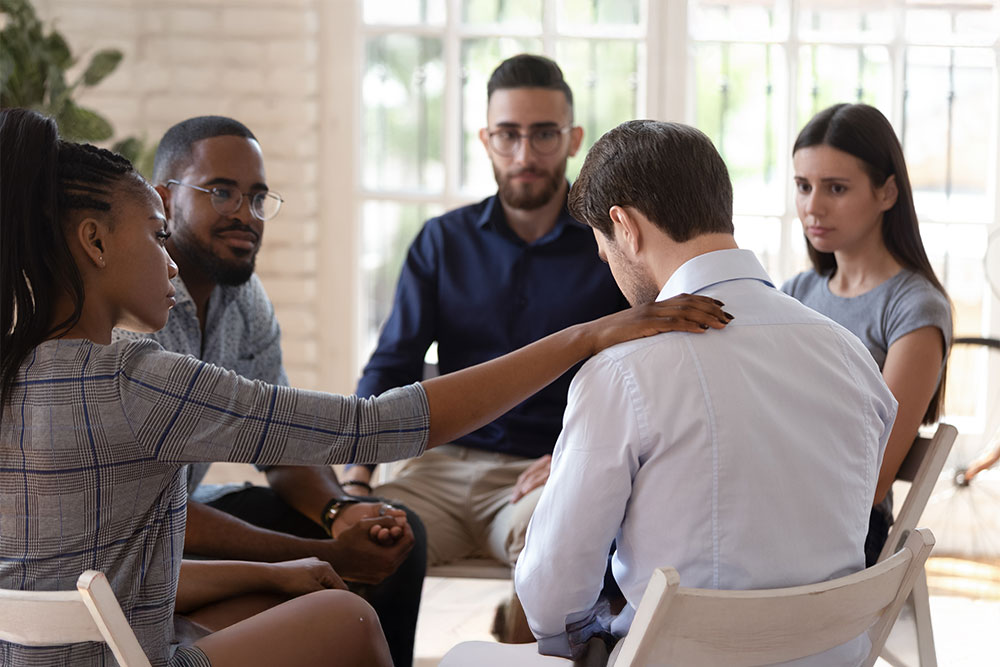
People who suffer from phobias deserve care and compassion. With the right treatments and support, a person can overcome irrational fears and get back to leading a normal life.
But many of us aren’t sure how to help someone struggling with a mental health problem. Making things more difficult is that there is still considerable stigma around mental health issues.
Where to Learn More About Mental Health Issues
Dealing with phobias, depression, or anxiety sometimes feels exhausting. However, improving your mental health can be as simple as making a few lifestyle changes and learning some coping strategies.
Completing one or more of our Mental Health Courses will give you a better understanding of mental health issues. These courses will teach you valuable skills to help others or help yourself, like managing your stress and being more resilient.
Our courses cover topics like maintaining a healthy diet, exercising correctly, and getting more sleep. They can even teach you healthier ways to use social media.
Sign up for Mental Health Training and help break the stigma around mental health issues.