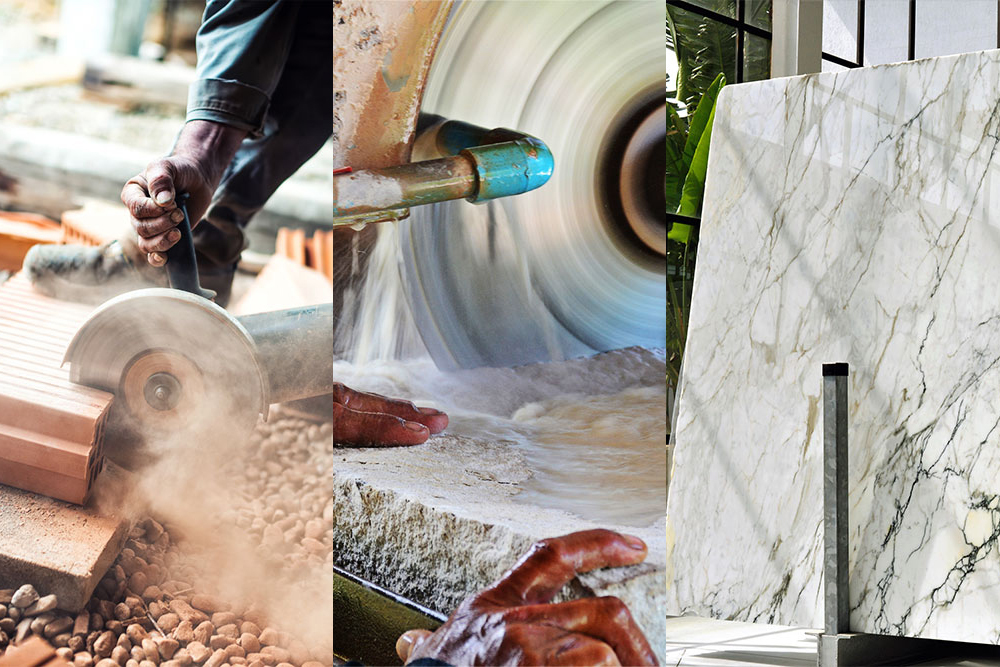
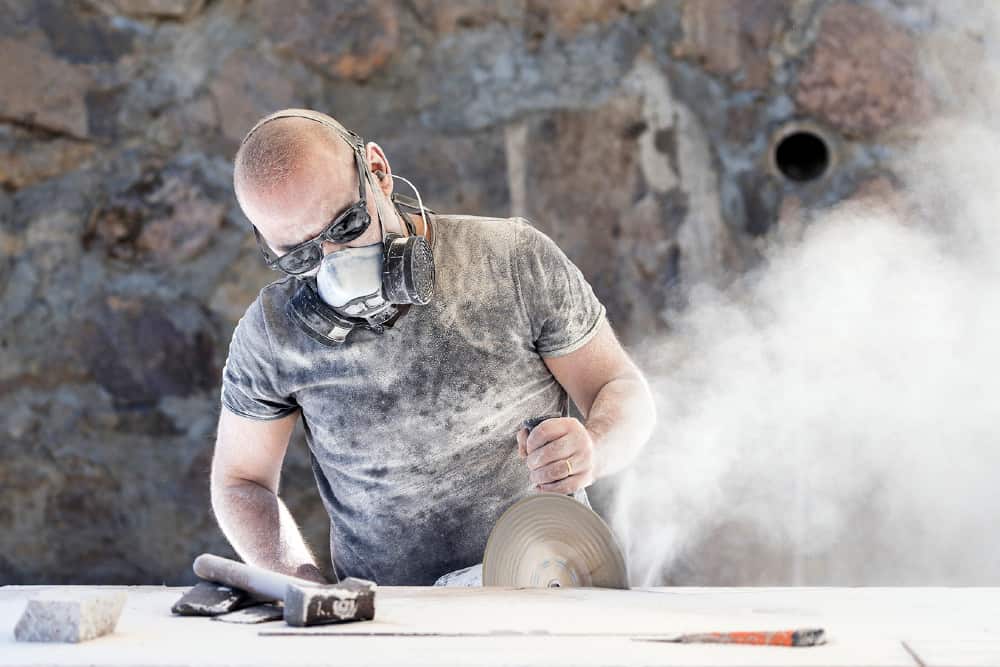
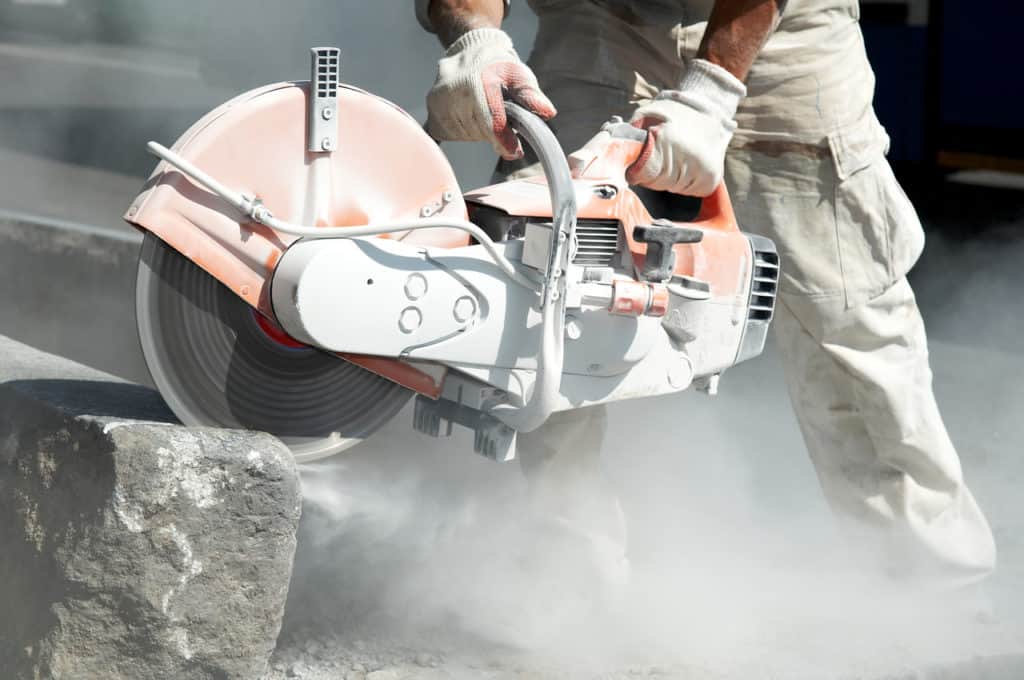
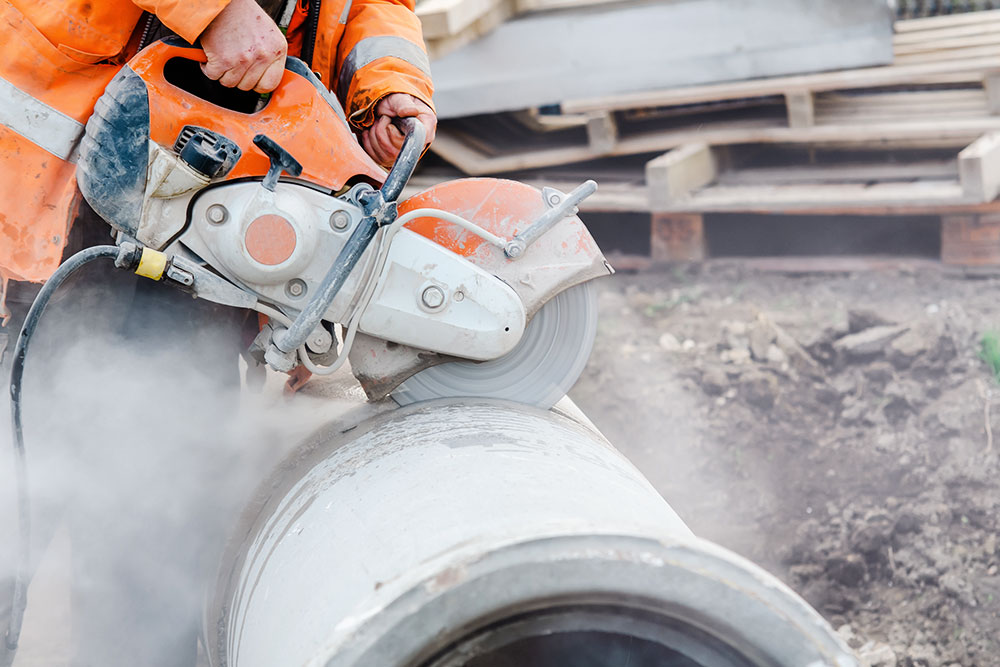
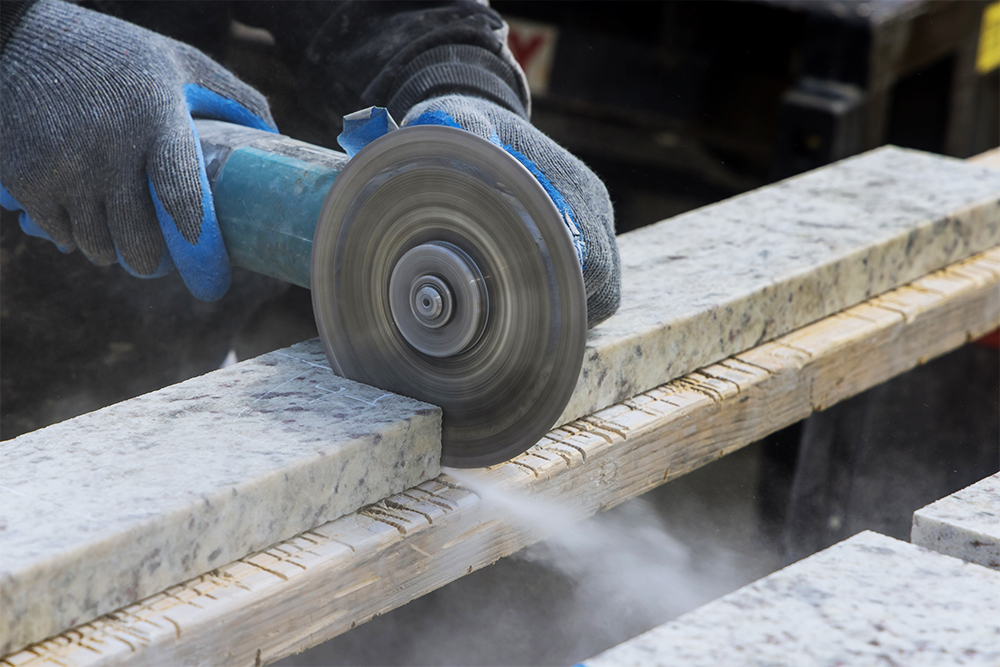
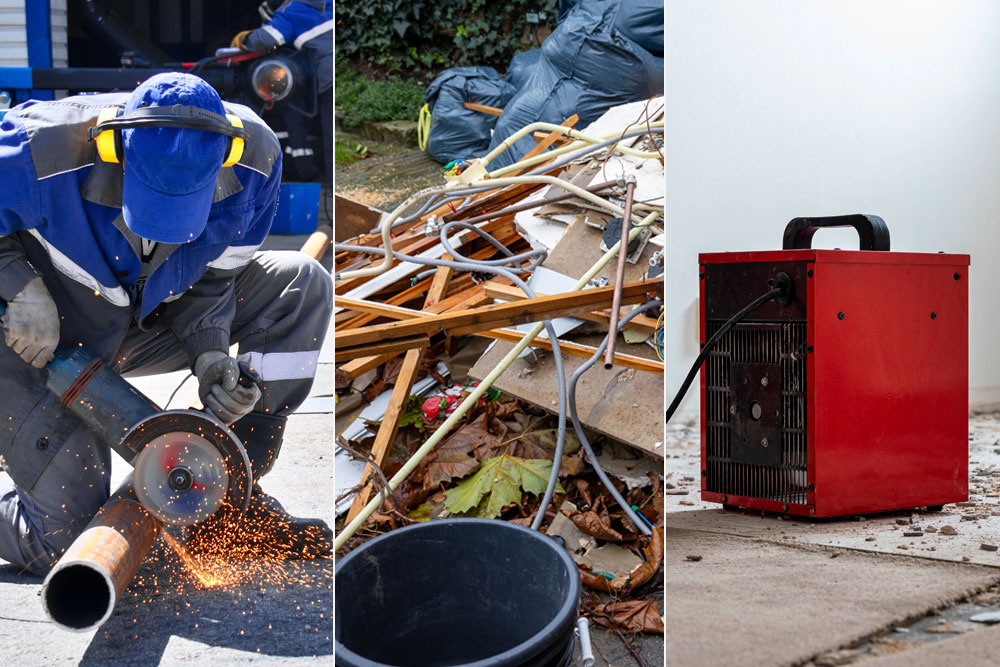
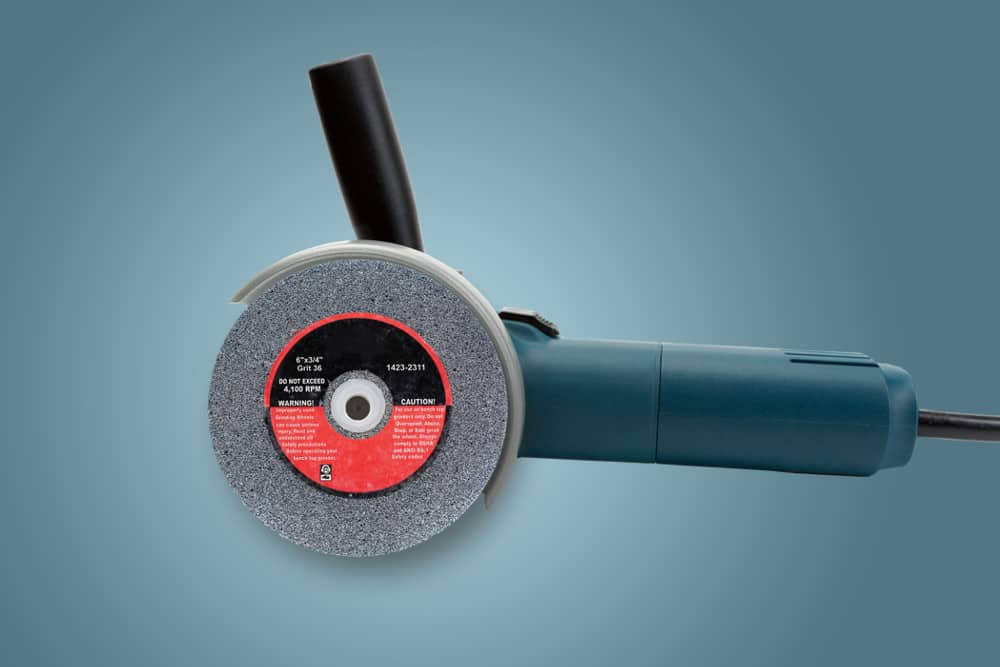
If you use abrasive wheels in the course of your work, then you need to ensure that all appropriate safety measures are taken. Abrasive wheels can be highly hazardous and, if used incorrectly, can cause severe injuries. Almost half of all accidents involving the use of abrasive wheels were caused by operator error or unsafe work practices, according to the Health and Safety Executive (HSE).
So, ensuring a comprehensive abrasive wheels risk assessment is in place and being used is vital. It is also a legal requirement stipulated by the Provision and Use of Work Equipment Regulations 1998 (PUWER) and the Health and Safety at Work etc Act 1974.
In this article, we will look at how to conduct a risk assessment to ensure optimum abrasive wheels safety measures are followed in the workplace.
Why Risk Assessments are Essential when Using Abrasive Wheels
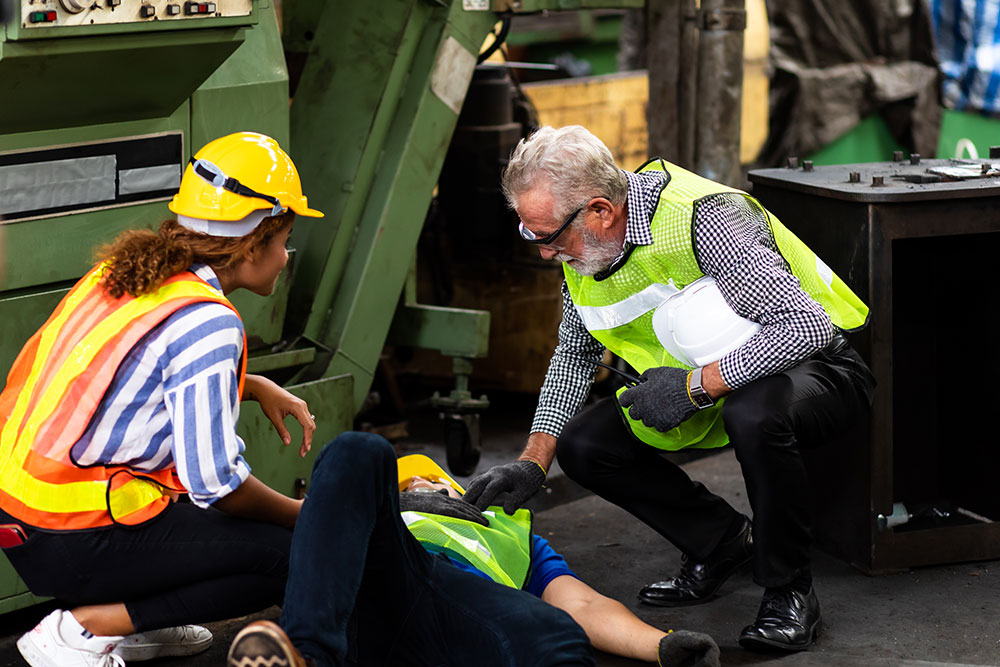
Poorly managed activities involving abrasive wheels can lead to fatalities, major injuries and serious damage to property and businesses. It is important that the hazardous nature of these activities is understood, and suitable precautions are taken to eliminate the risks.
All risk assessments dealing with the use of abrasive wheels should be conducted in a methodical and precise manner. The aim of a risk assessment is to identify any potential hazards and implement abrasive wheels safety procedures to eliminate or mitigate these risks.
The Five Steps of Abrasive Wheels Risk Assessments
There are five steps involved in an abrasive wheel risk assessment:
- Identify the hazards
- Decide who might be harmed and how
- Evaluate the risks and decide on precautions
- Record your findings and implement them
- Review your risk assessment and update it if necessary
Starting the Risk Assessment
To begin, list out the main job or tasks in your workplace that are likely to involve abrasive wheels. This will enable you to look at each activity to see where there might be problems.
For each task, you will need to walk through the activities involved in order to identify any hazards. Involve your colleagues in these situations. They often have valuable knowledge and experience in these activities.
Step One: Identify the Hazards
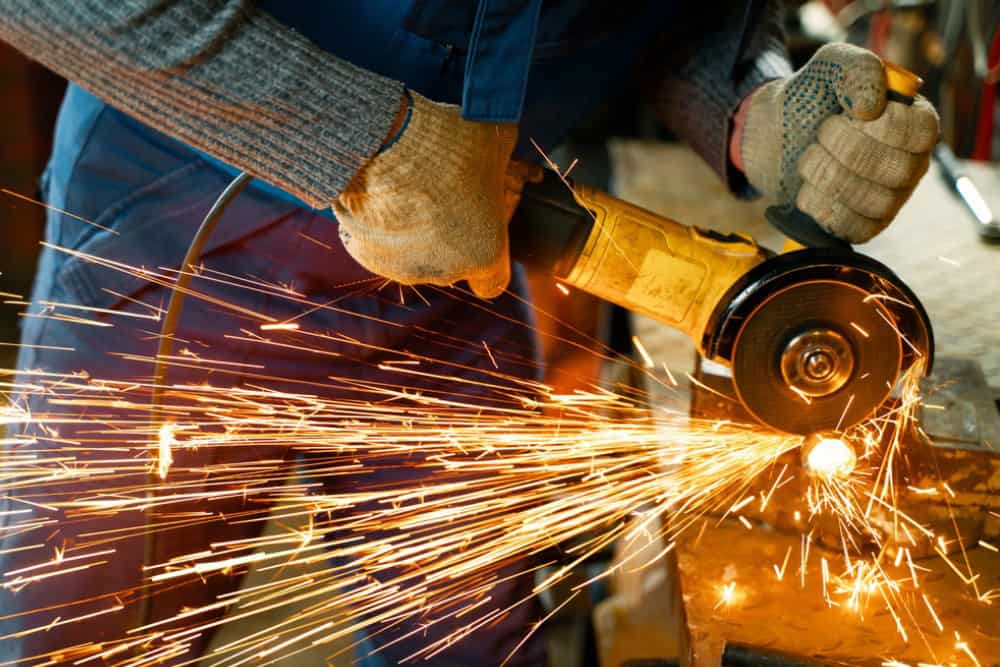
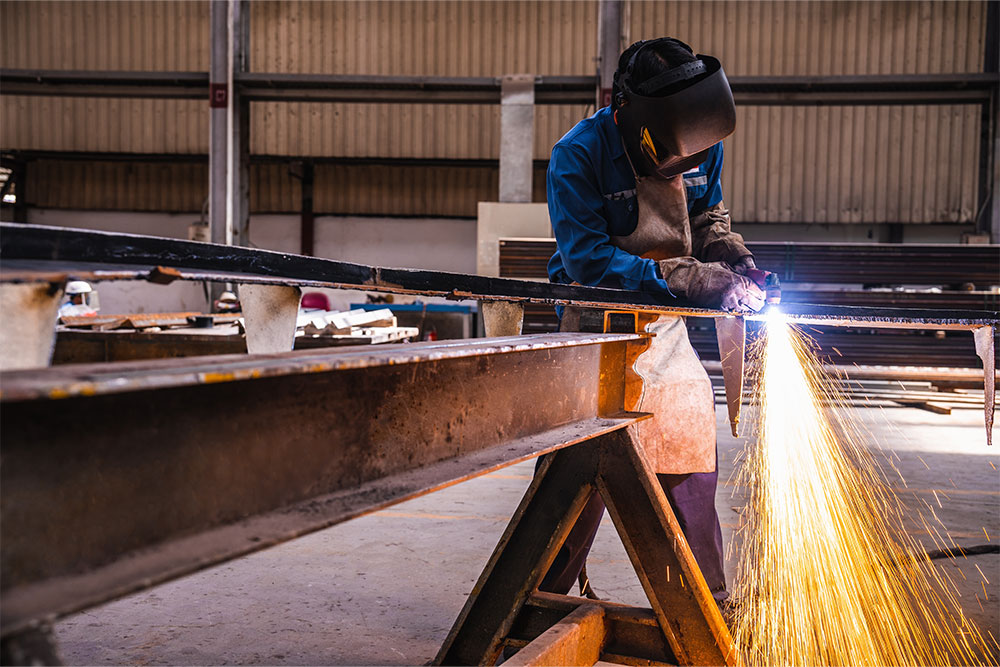
The first stage of the risk assessment process is to identify the hazards. Abrasive wheels revolve at very high speeds, so there is a range of obvious mechanical hazards. Some of the hazards that you need to be aware of when working with abrasive wheels include:
- Mechanical Hazards
- Electricity
- Fire and Heat
- Dust
- Noise
- Vibration

Loose clothing or jewellery can catch on moving parts. Impact injuries can result from flying debris or pieces breaking off from a damaged or defective wheel. The workpiece itself can also shift or be ejected. Cuts and abrasions from direct contact with the wheel can occur because of unintended slips or sudden movement.
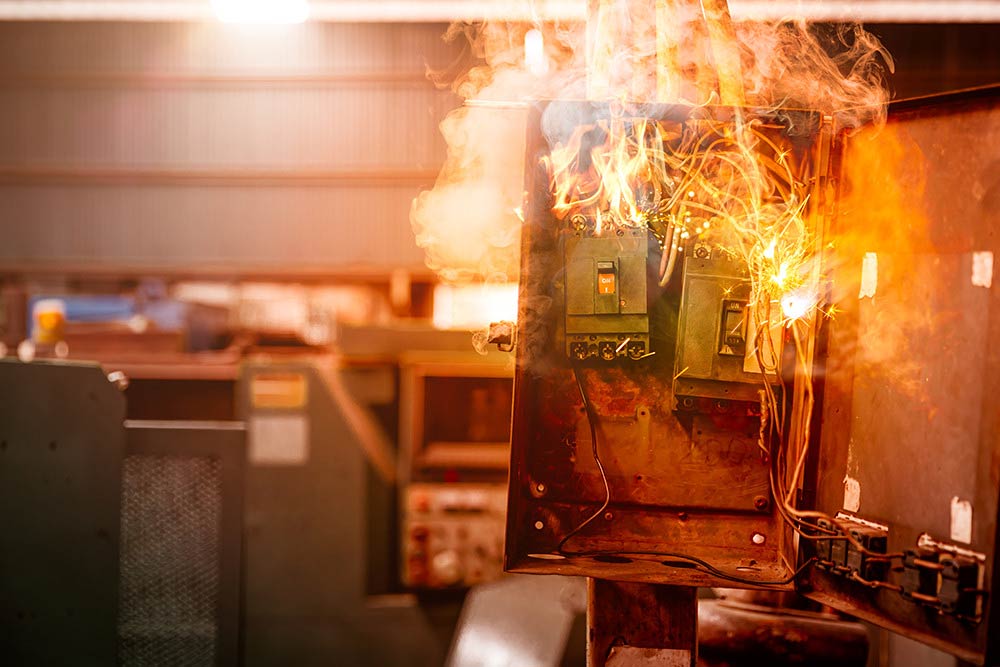
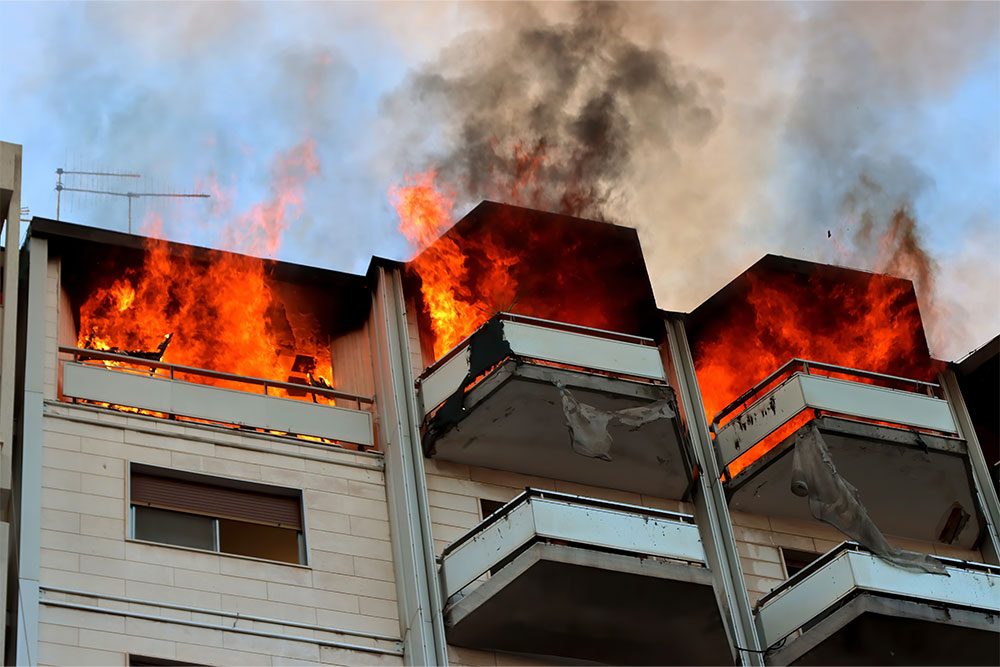
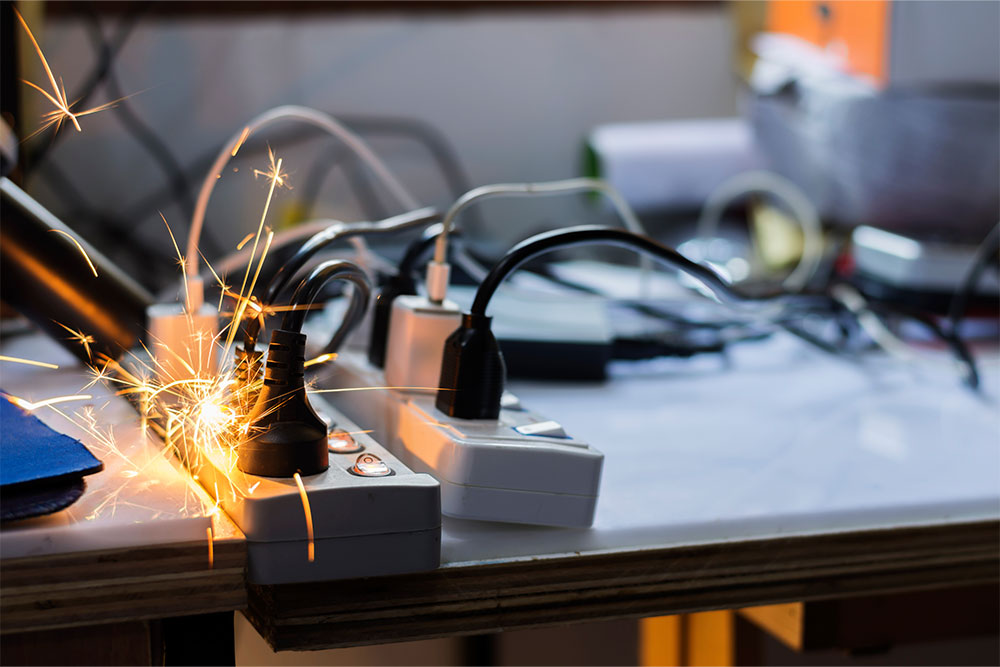
Combustible materials can readily catch fire if they come in contact with sparks or hot particles from activities like cutting, welding or grinding. Fires occasionally start as a result of heat travelling through conductive materials, such as steel or metal pipework that is in contact with combustible materials. Fires can also occur after hot work has been completed. Sparks from the activity can land on combustible materials and smoulder for a considerable time before igniting.
Step Two: Decide Who Might Be Harmed and How
When considering abrasive wheels safety issues, it is important to note that not only the operator themselves are at risk. Abrasive wheels can also be hazardous to people in the immediate vicinity. High levels of noise and dust can damage the ears and lungs of bystanders. Flying debris from the workpiece or a broken wheel can result in co-workers being injured or equipment being damaged.
Consider any site visitors or contractors. What precautions must be taken to ensure their safety?
Step Three: Evaluate the Risks and Decide on Precautions
There is always a significant risk of injury with any work that involves abrasive wheels. While all workplaces are different, there are certain abrasive wheel safety measures that should always be adhered to.
These measures include precautions for:
- Drawing in Hazards: Operators should not wear any loose clothing or jewellery. Hair, clothing and gloves must be kept away from moving parts.
- Accidental Contact with the Wheel: Operators should perform their work in a stable or balanced position and ensure they do not overreach. Their footing should be stable and there should be no risk of slipping. Machine guards should be fitted to machinery containing abrasive wheels. These guards must not be removed. Operators must understand the risks of vibration and white finger injuries.
- Handle Kickback and Slippage: Auxiliary handles should be used to exert maximum control over torque reaction or kickback. The handle areas must be kept dry, clean and free from oil or grease.
- Wheel Breakage: The wheel used should be rated for the speed of the tool. The correct type of abrasive product should be used, and the wheel should be inspected to ensure it is in good condition.
- Faults: Wheels and blades should only be replaced by trained staff. Wheels and blades should be inspected before every use.
- Flying Debris: The work area should be cordoned off so that flying debris cannot strike bystanders.
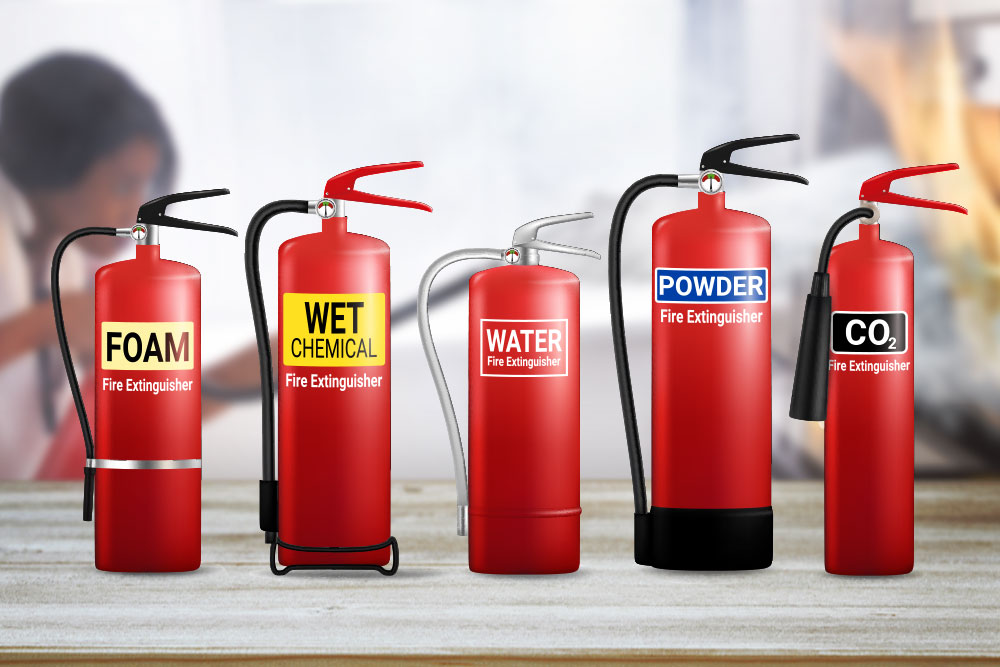
- Fire: A fire extinguisher should be available at all times and all flammable materials removed from the area.
- Noise: Ear protection must be worn.
- Emergencies: A co-worker or assistant should be available to advise the operator if alarms, sirens or other types of warnings are sounded.
Other risk controls that must be taken include:
- Adequate Training: Only persons who have undertaken abrasive wheel training should be allowed to operate machinery containing abrasive wheels.
- Safe Storage: Abrasive wheels should be stored correctly to ensure they stay in good condition.
- Personal Protective Equipment: Appropriate personal protective equipment must be provided, including face protection, gloves and safety shoes. If significant amounts of dust will be generated by the work, then a suitable face mask that filters dust should be provided and must be worn.
- Employee Welfare: Regular breaks should be allowed
Step Four: Record Your Findings and Implement Them
A detailed record of all findings should be made. It should be noted that this is a mandatory step if the business has five or more employees.
Notes should be made on all hazards that were identified, who may be harmed by these hazards, and the steps taken to mitigate or eliminate risks. To ensure you keep a correct record, it may be helpful to use an abrasive wheels risk assessment template that can be downloaded from the HSE website or other such resources.
Step Five: Review Your Risk Assessment and Update it if Necessary
Risk assessments should be regularly reviewed, at least on an annual basis. If any changes have occurred in the workplace, such as new procedures or new equipment, then the risk assessment should be redone and all abrasive wheels safety measures updated.
A review should also be conducted and updates implemented if there were any near misses or accidents that occurred.
Ensure All Staff Have Appropriate Abrasive Wheel Training
Just as it is imperative that an abrasive wheels risk assessment be undertaken it is also mandatory for all staff to participate in abrasive wheels training.
By taking part in an abrasive wheels health and safety course, employees can learn the hazards associated with this type of machinery, be instructed on how to perform a risk assessment and be aware of precautions that need to be taken to ensure the workplace is safe.
Completing the Human Focus Abrasive Wheel Training course will provide participants with the knowledge and skills they need to operate abrasive wheels safely. Additional training can also be taken to further enhance health and safety knowledge and skills, such as the IOSH Managing Safely Course offered by Human Focus.
To learn how to properly conduct a risk assessment, trainees can complete the Human Focus Work Equipment Risk Assessment course. All of these courses can be taken in segments online, at your convenience and are fully accredited and certified.