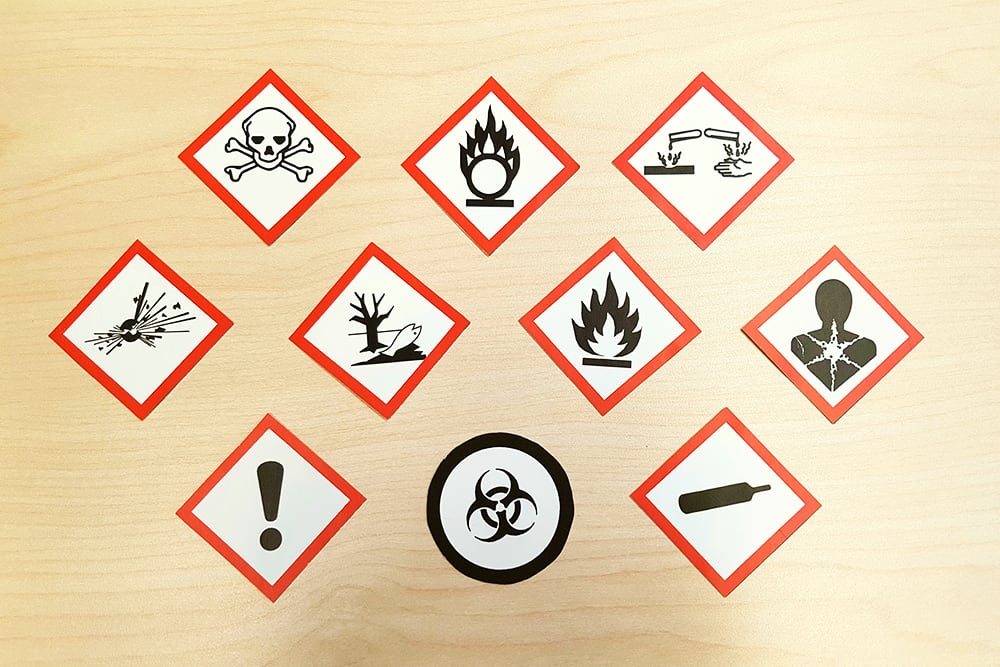
Maintaining COSHH compliance is a legal requirement for all UK businesses. This means that if you use any hazardous substances in your workplace, you must understand how to properly control their use.
Fortunately, tackling compliance with COSHH can be an easy process, if you do it systematically. It is generally accepted that there are eight steps to COSHH compliance. In this blog, we explain what these steps are and how to protect your staff and your organisation.
Why the Eight Steps to COSHH Compliance Are Vital
All workplaces must abide by the Control of Substances Hazardous to Health Regulations (COSHH). As well as significant health risks, failing to maintain COSHH compliance can result in severe penalties such as unlimited fines and criminal charges.
The Costs of Breaching COSHH
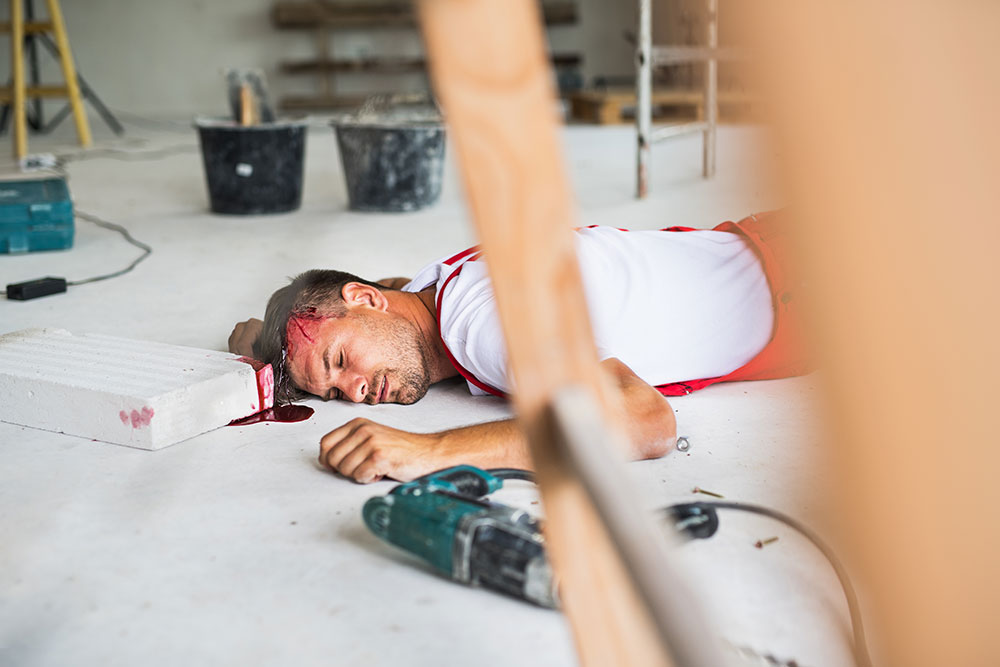
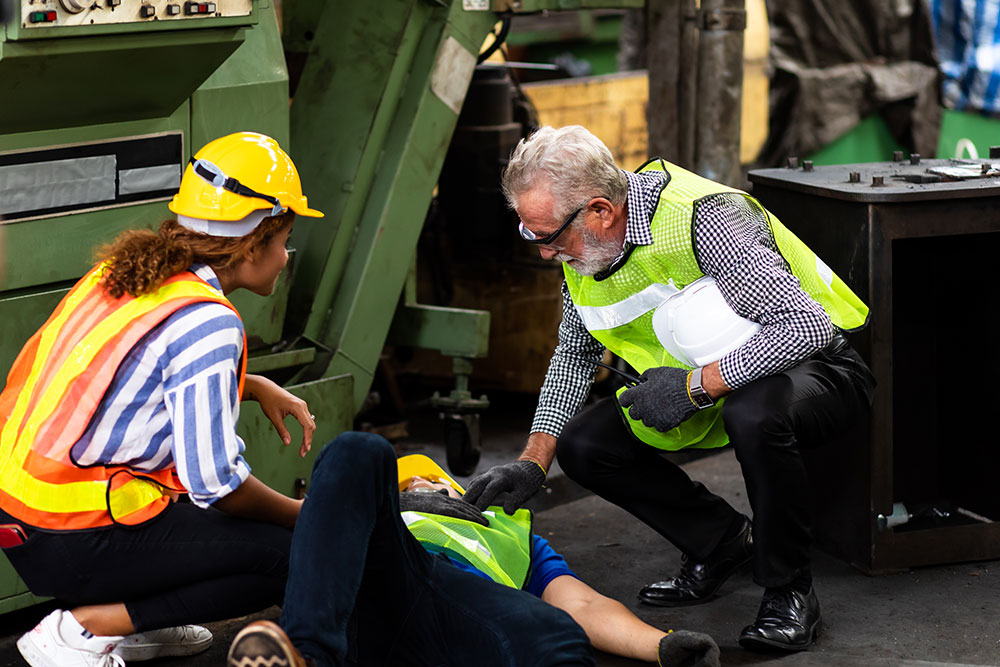
A recent example of COSHH penalties was demonstrated by the case brought against Brick Restoration Ltd by the Health and Safety Executive (HSE). In 2017, Brick Restoration Ltd employee Alexandru Sorin died as a result of being exposed to dichloromethane (‘DCM’) vapour, while stripping paint in the basement of a London property.
The HSE determined that Mr Sorin’s death was caused by the failure of Brick Restoration Ltd to implement effective measures to eliminate or control the risk of DCM exposure. The company was found guilty of breaching COSHH Regulation 7(1) and fined £50,000.
But that’s not all. The two directors of the company were both sentenced to 200 hours of community service and made to pay £2,805.64 in costs.
By following the eight steps to COSHH compliance you can keep your employees safe and avoid breaking the law.
The Eight Steps to COSHH Compliance
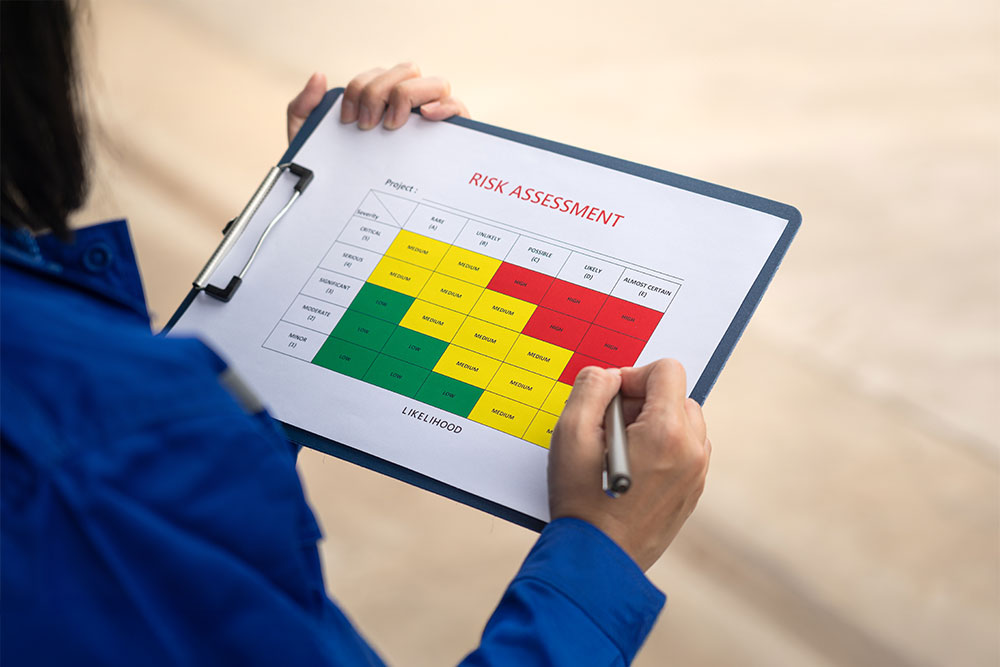
Step 1: Conduct a COSHH Risk Assessment
A COSHH risk assessment aims to identify all hazardous substances stored and used in the workplace. Employers can conduct the risk assessment, or they can appoint a competent employee to do it. If neither the employer nor the employees have the necessary skills and knowledge, a third party can be brought in to conduct the COSHH risk assessment.
The COSHH risk assessment must include:
- A list of all hazardous substances, whether they are stand-alone chemicals or produced as a result of work activities
- Evaluations of the health risks of all hazardous substances
- A list of who may be harmed and how
- The levels of exposure to hazardous substances
- A record of all control measures that are taken
Step 2: Eliminate Any Risks
Best practice is to eliminate any risks posed by hazardous substances. Employers must first consider if a task involving hazardous substances can be avoided completely. In some cases, an alternative substance can be used, or a work process can be changed to remove the need to use a hazardous substance.
For instance, consider an industrial process that cleans components in a toxic chemical solution. If a mild soap and water solution could be used instead, this would eliminate the hazard posed by the chemicals.
Step 3: Implement Control Measures
If it’s impossible to eliminate the risk, then employers are required to implement control measures that reduce the risk to ‘as low as is reasonably practicable’. Control measures should be proportionate to the risk posed by the hazardous substance.
Control measures can include:
- Ensuring there is sufficient ventilation in work areas
- Providing personal protective equipment (PPE)
- Lowering the amount of exposure to the substance as much as is reasonably possible
Step 4: Review Control Measures
All control measures must be regularly reviewed to ensure they are still effective. Reviews must be conducted if there are any changes to work processes or if any new hazardous substances are introduced to the workplace.
A review must also be conducted if an employee reports that they do not feel the current control measures are adequate.
Reviews can include:
- Conducting a partial or full risk assessment
- Making a complete check of all equipment and PPE
- Conducting environmental testing such as taking air samples
- Record all findings.
Records of reviews and risk assessments must be kept for a minimum of five years.
Step 5: Develop Emergency Procedures
Even if you have highly effective control measures, accidents or emergencies can happen. Employers need to make sure that their teams are prepared and can react appropriately if an emergency arises.
This is a legal requirement under Regulation 13 of COSHH.
Emergency measures can include:
- Implementing procedures to deal with spills of hazardous substances
- Providing first aid training
- Setting up emergency communication systems
- Keeping safety and first aid equipment on site
- Performing regular safety and emergency drills
Step 6: Monitor Workplace Exposure Levels
The harmful effects of some hazardous substances only occur after years of prolonged exposure. COSHH requires employees to ensure that exposures to harmful substances such as mutagens, carcinogens or asthmagens be kept ‘as low as is reasonably practicable.’
Employers must ensure that Workplace Exposure Limits (WELs) to hazardous substances are not exceeded. A WEL is an exposure limit set by the government, which should not be exceeded unless proper controls are in place. For instance, the WEL for silica dust is 0.1 mg/m3, expressed as an 8-hour time-weighted average.
Professional monitoring of the air quality in work environments should be regularly conducted. It is advisable to hire a specialist monitoring service to ensure your workplace is safe.
Step 7: Conduct Health Surveillance
The physical health of your employees should be assessed regularly. Performing health surveillance includes checking that employees have not developed skin conditions such as dermatitis, that their respiratory systems are not adversely affected and that they show no signs of developing serious health issues.
Health checks should be performed by an occupational health professional such as a doctor or nurse. Employers must make sure that the health professional is experienced in occupational medicine.

Step 8: Provide Information and Training
COSHH stipulates that all employees must be properly informed of any workplace risks. Employees must be provided with adequate training on how to handle, store and work with hazardous substances.
Training must cover the correct use of any PPE, including proper storage methods and how to check for faults. Staff must learn how to properly use any mechanical equipment or tools required to complete their duties.
Sign Up for COSHH Training Today
You can ensure that your team receive relevant and accredited COSHH training by signing up for a Human Focus course.
Our COSHH training course provides participants with a complete understanding of COSHH principles. Trainees will learn how to identify hazardous substances and conduct risk assessments. The Human Focus COSHH course also details the best practices for working with hazardous substances.
On successful completion of the course, trainees can immediately download a certificate recognised by industries and authorities across the UK.