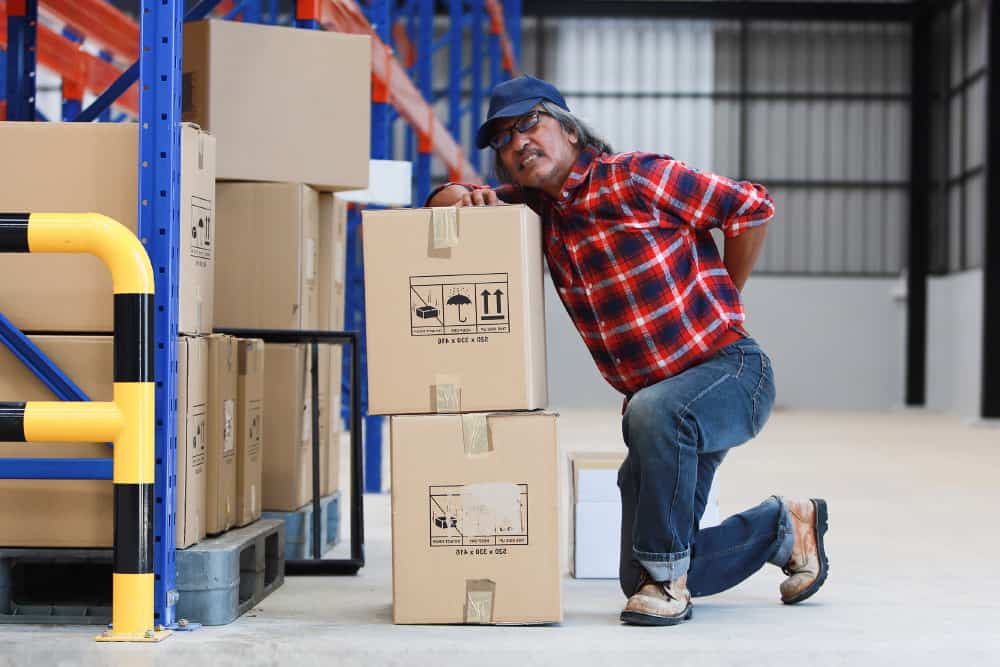
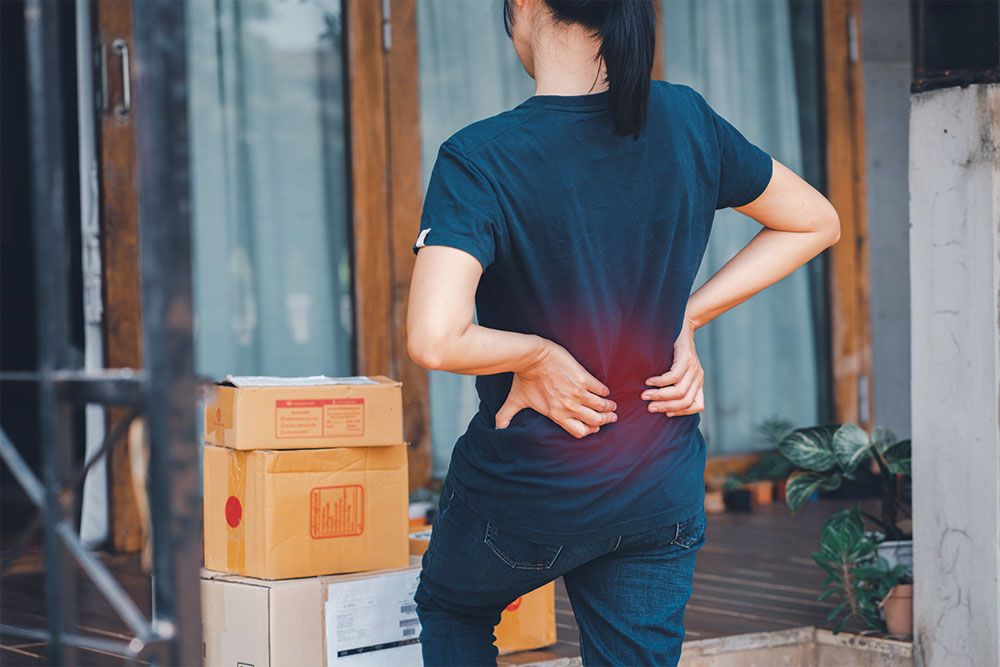
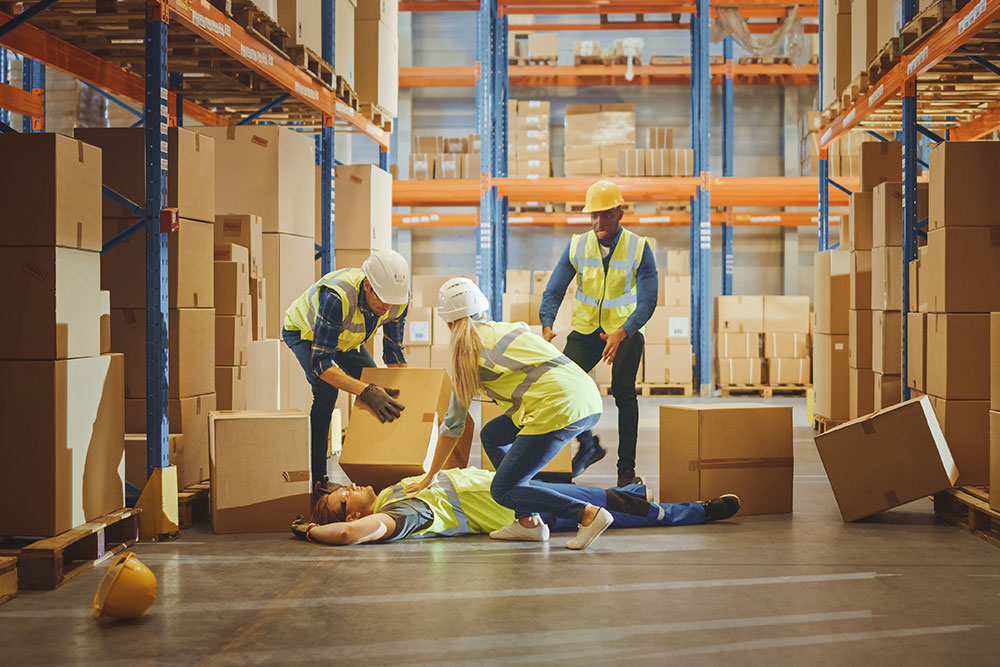
Manual handling at work accounts for nearly a fifth of all workplace injuries. When injury happens, it results in pain and suffering for the individual, lost production, sickness absence and possibly fines for failure to comply with health and safety legislation. Consider a case in Norwich where an employee of an engineering company had his fingers crushed beneath a steel frame weighing 250 kilograms. The resulting investigation found that the company in question had failed to protect workers or reduce the likelihood of injury. As a result, the company was fined £20,000 – a significant burden for any small to medium sized business.
Every employer must protect their employees from manual handling risks under manual handling at work regulations in the UK. It’s a financial, legal and moral duty. In this article, we will take a look at what you should know about manual handling in the workplace, what the law says and how to protect against this hazard.
What is Manual Handling?
Manual handling is defined by the Health and Safety Executive (HSE) as any task that involves ‘transporting or supporting a load by hand or bodily force’. This definition covers all types of carrying, lifting, lowering, pushing or pulling. Anytime an employee moves a ‘load’ without the use of equipment or a machine, the task is designated as manual handling. A ‘load’ is any moveable object, human or animal.
What Are the Manual Handling Laws That Employers Need to Know?
Manual handling at work is covered by two main pieces of UK legislation:
- The Health and Safety at Work Act 1974 – This is the main piece of health and safety legislation in the UK and broadly covers the obligation of employers towards their employees and the public
- The Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992 – This legislation provides specific guidelines and rules for manual handling at work
What do the Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992 Cover?
Under the Regulations, employers must reduce all risks from manual handling in the workplace. The manual handling at work regulations states that employers can achieve this by following a health and safety hierarchy. The regulations are overseen and enforced by the HSE.
Under the Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992, employers must:
- Avoid the need for tasks involving hazardous manual handling so far as is reasonably practicable
- Assess the risks involved in any unavoidable hazardous manual handling task
- Reduce the risk of injury from a hazardous manual handling task so far as is reasonably practicable
The guidance contained in the regulations is intended for employers, managers, safety representatives and employees.
Employee Responsibilities for Safe Manual Handling in the Workplace
Employees also have health and safety responsibilities. Health and Safety legislation requires employees to:
- Follow the safe systems of work that have been put in place
- Lift objects using correct manual handling techniques
- Use all lifting equipment in the manner in which it is intended
- Act in a manner that does not endanger themselves or anyone else
What Does ‘So far as is Reasonably Practicable' Mean?
The term ‘so far as is reasonably practicable’ is important to understand when meeting your health and safety legal duties. It’s a key part of numerous pieces of legislation. It’s so ubiquitous that it’s often abbreviated to SFAIRP.
The concept of ‘so far as is reasonably practicable’ is based on the idea that it’s impossible for an employer to completely remove all risks from the workplace. They are, however, expected to do as much as they can to remove risk in a practical and common-sense manner.
In a workplace environment such as a warehouse, it’s not practical to eliminate all tasks involving manual handling. Employees need to move objects in order to complete their work. Removing the risks, by eliminating the tasks completely, is not a reasonable proposition. The warehouse wouldn’t be able to function or turn a profit, if employees never conducted any manual handling tasks.
Employers must act in a practical way to ensure these tasks are made as safe as possible. This can be done by ensuring that employees follow the correct manual handling techniques or, for example, by providing them with lifting equipment to use when carrying out their tasks.

How to Decide What is 'Reasonably Practicable'
Judging what is ‘reasonably practicable’ can sometimes be difficult. UK courts have ruled that employers must take into consideration the severity of the risk, in relation to the measures needed to safeguard against it.
The balance should always be weighted towards the health and safety side, regardless of the cost or inconvenience. The more severe the risk, the less consideration should be given to the expense of safety measures. If the risk is minimal and eliminating it entirely would cost a significant amount of money, then the employer would not be expected to put those measures in place.
This doesn’t mean that health and safety control measures can be discarded simply because they’re expensive. Employers are expected to do everything they can to implement health and safety measures and can only neglect this duty when the cost or practicality of such measures is disproportionate to the risk itself.
Penalties for Breaching the Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992
The penalties for breaching the Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992 are severe.
Employers could have to pay fines of between £5,000 and £20,000 if the matter is tried in a magistrates’ court. Serious breaches that are tried in a Crown Court can result in fines that have no legal limit. The court can set the amount at whatever it wishes. These costs cannot be recouped by insurance. Fines can be issued to employers as well as employees.
If a breach is reported, then an investigation will be carried out by local and enforcing authorities in conjunction with the HSE. The HSE can request to inspect a premises at any time and must be given access if they wish to perform an inspection.
The best way to avoid breaching the Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992 or the Health and Safety at Work Act 1974 is to ensure your people are fully trained in proper manual handling techniques.
Online Training for Manual Handling in the Workplace
Failure to adhere to the rules as laid out in the Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992 can result in workplace injuries and significant penalties. You can make sure that your staff know how to perform manual handling tasks correctly, by enrolling them on a Human Focus manual handling course.
These courses provide trainees with in-depth knowledge of all aspects of manual handling at work. You can select a Manual Handling Training course specific to your industry, that runs for approximately 20 to 30 minutes and can be taken online in segments, at your convenience.
Avoid injuries and fines. Keep your workplace safe and sign up for a manual handling course today.