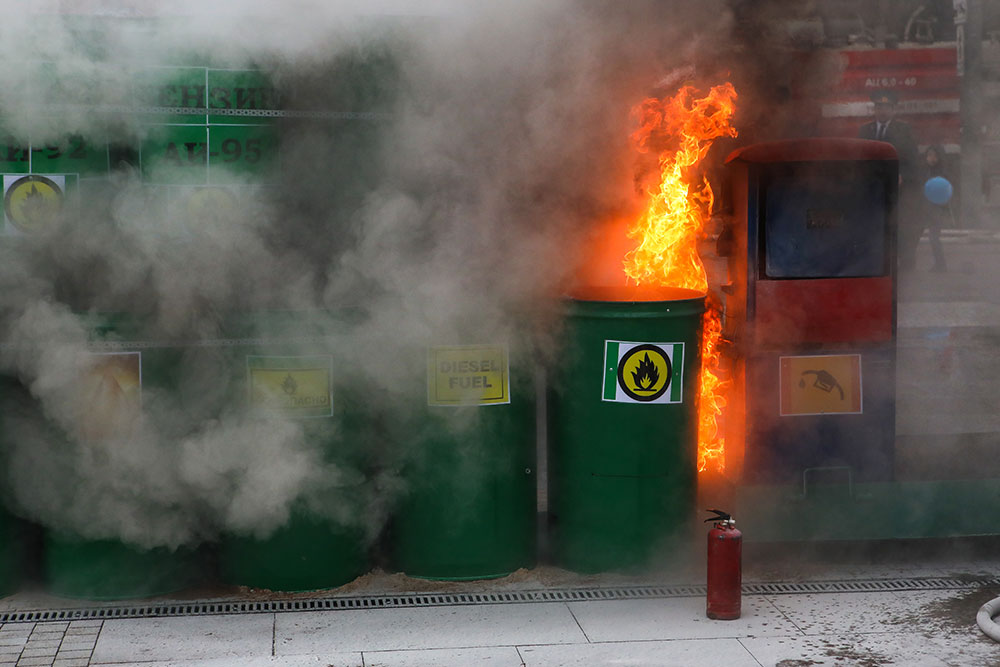
UK health and safety legislation requires all businesses to take appropriate fire safety measures. The law states that employees and employers must collaborate to develop and implement an effective fire strategy.
But knowing who has to perform what role regarding fire safety can be challenging. We’ve put together the below guide to help you understand who is responsible for fire safety in the workplace.
Why Fire Safety in the Workplace is So Important
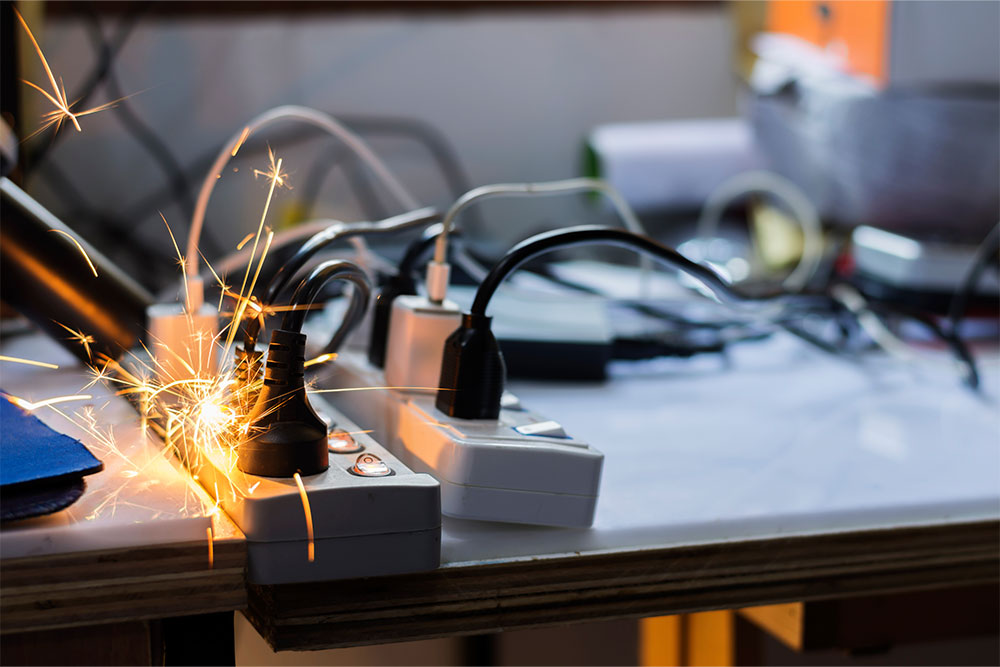
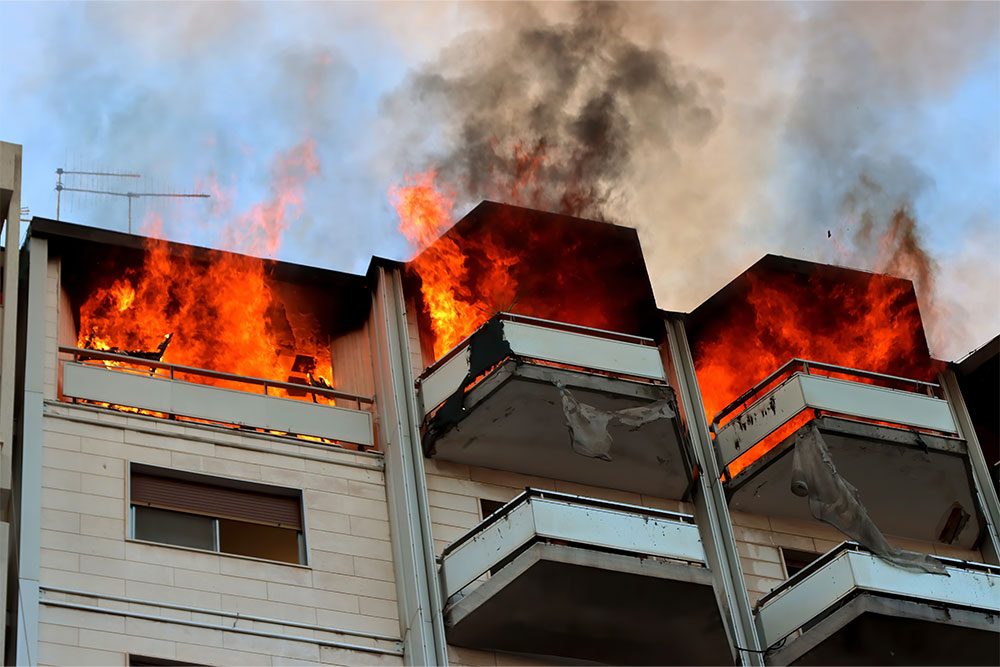
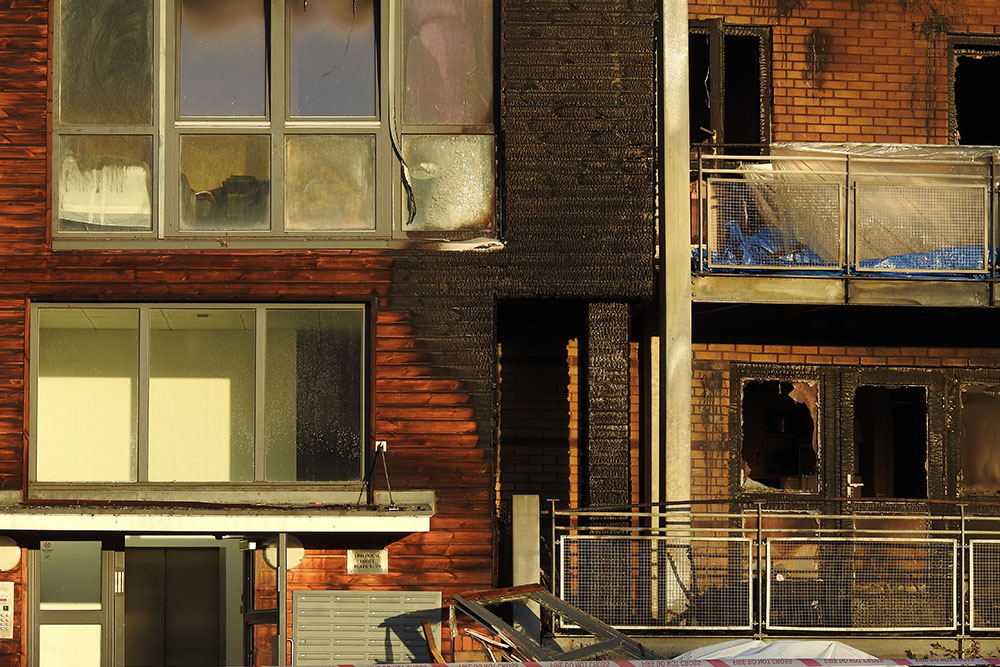
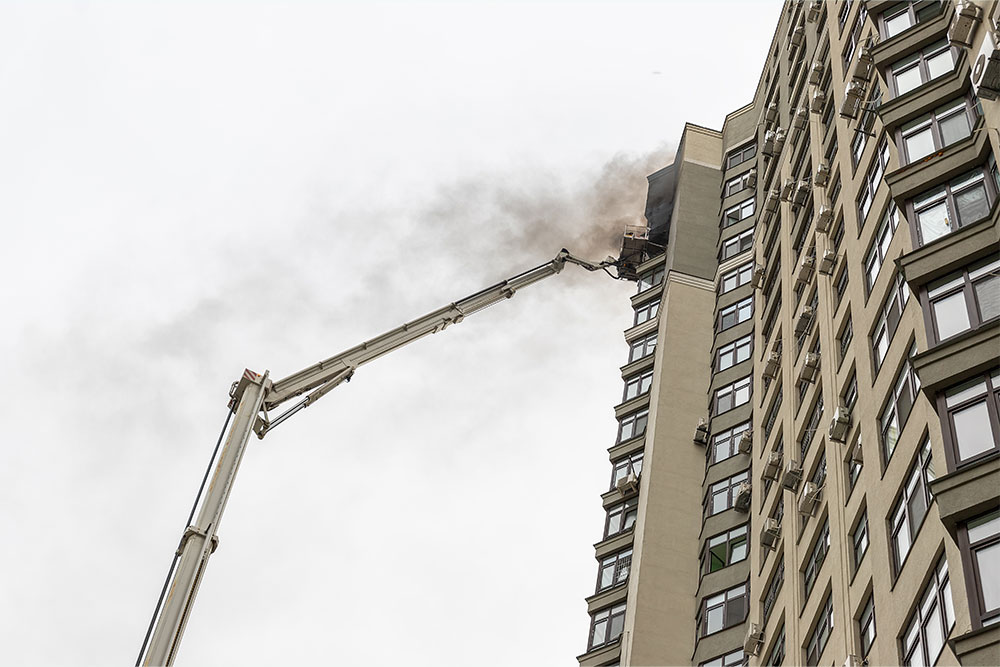
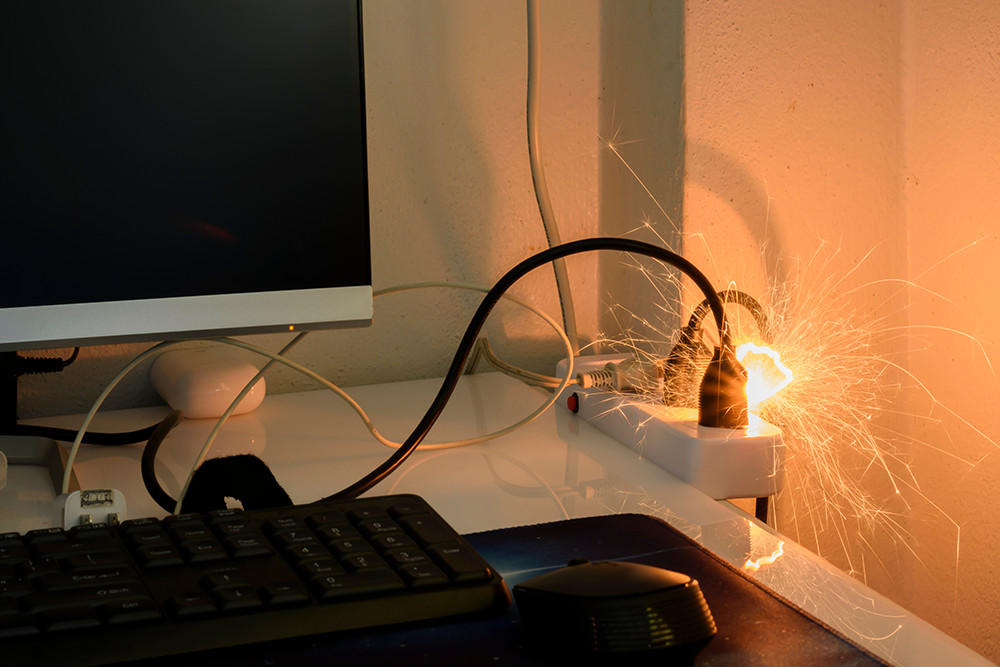
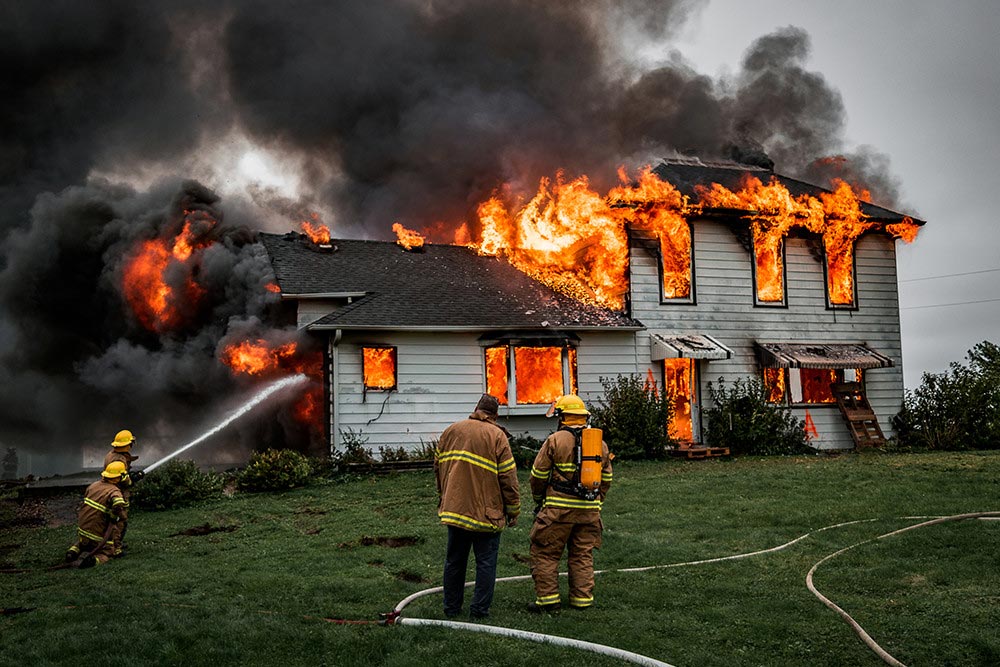
There are approximately 25,000 non-domestic fires in the UK every year. The impact that a fire can have on a business can be devastating. A fire starts in seconds and can spread through a large building in minutes. Most companies cannot recover after a significant fire, even with insurance payouts. As well as the loss of people’s livelihoods, fire can cost people their lives in the worst cases.
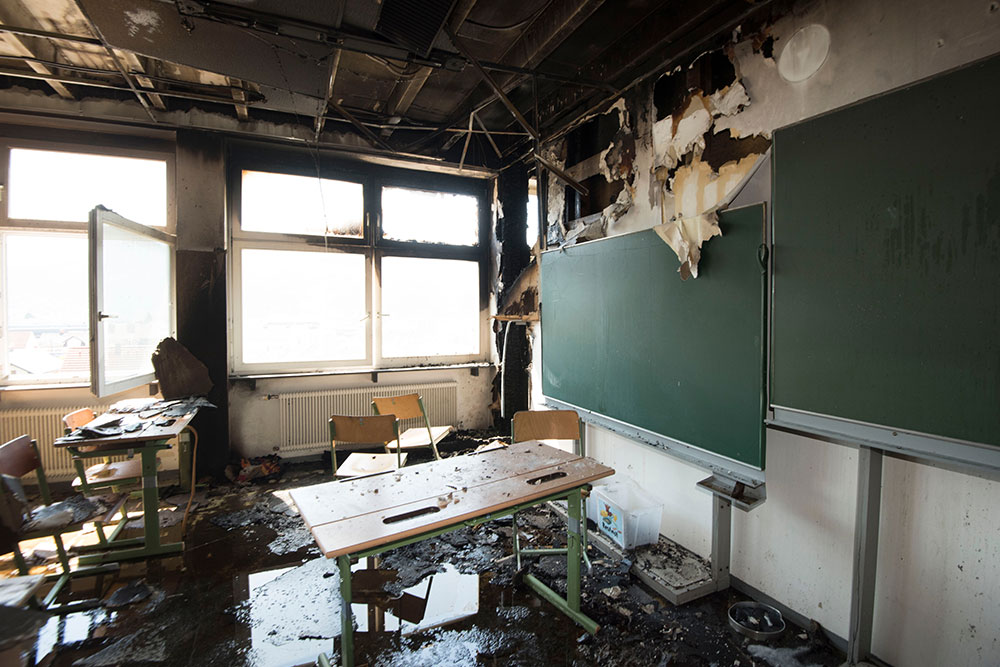
A recent case shows why being vigilant about fire safety in the workplace is so crucial. Garswood Gates in Ashton-in-Makerfield was a family-run company operating for over 40 years before a fire completely destroyed the business in February 2023. The exact cause of the fire remains unknown, but it is thought to have been accidental. At the time of writing, the owners of Garswood Gates are unsure if they can rebuild their business.
Who Is Responsible for Fire Safety in the Workplace?
The reality is that fire safety in the workplace is everyone’s responsibility. However, there are specific responsibilities that UK health and safety legislation places on both employers and employees.
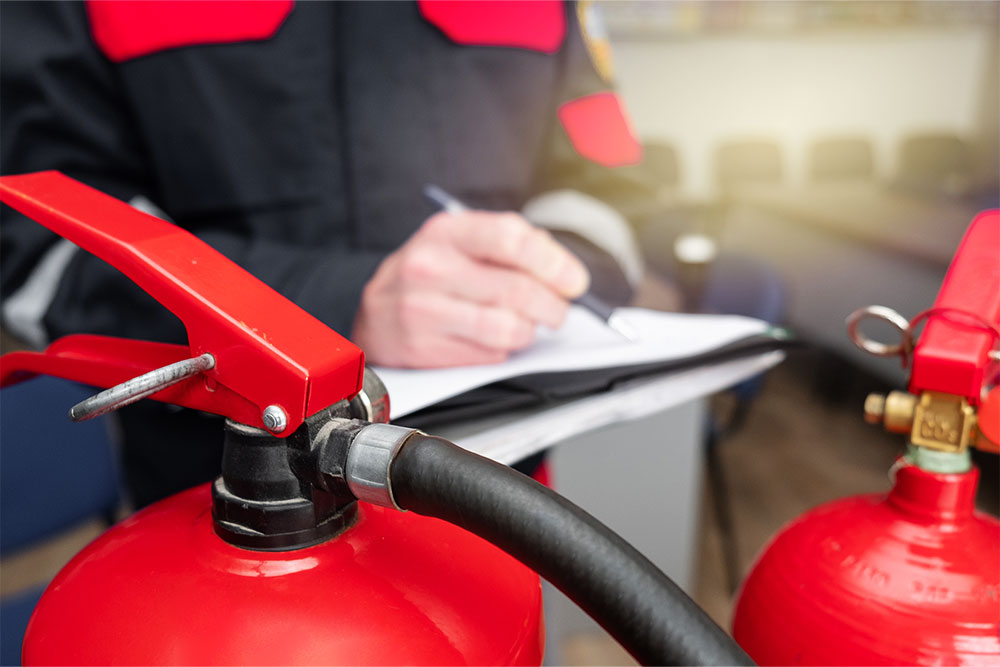
The Fire Safety Responsibilities of Employers
Under the Health and Safety at Work etc. Act 1974, UK employers are legally responsible for ensuring the workplace is safe. The act specifically states that employers must identify all risks in the workplace and take appropriate measures to eliminate or control these risks ‘so far as is reasonably practicable.’
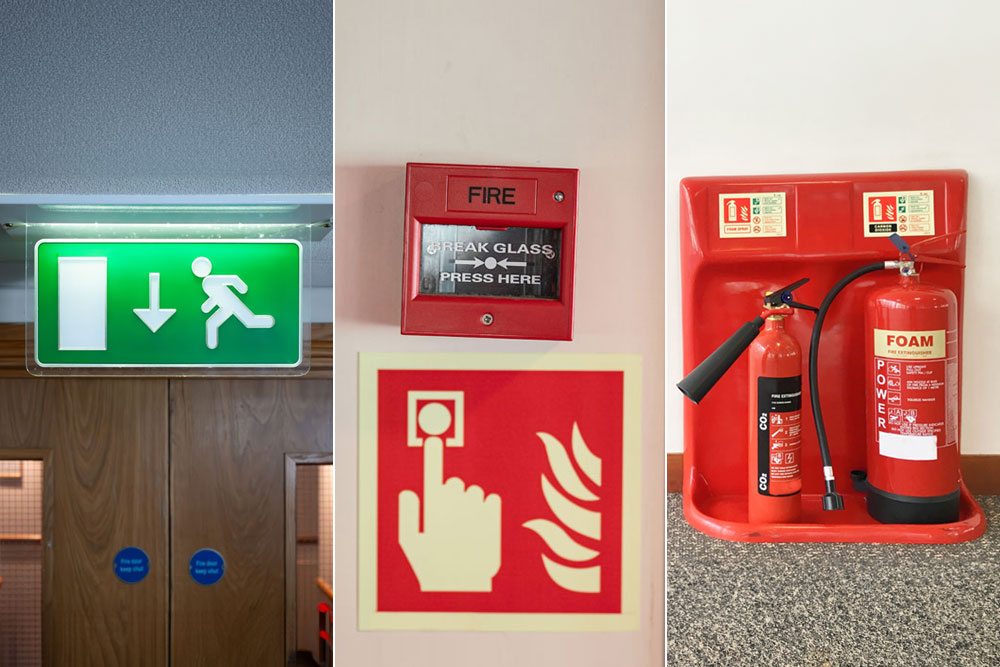
The Regulatory Reform (Fire Safety Order) 2005 (RRO) provides specific details on what employers need to do regarding fire safety in the workplace. The RRO stipulates that employers must ensure that:
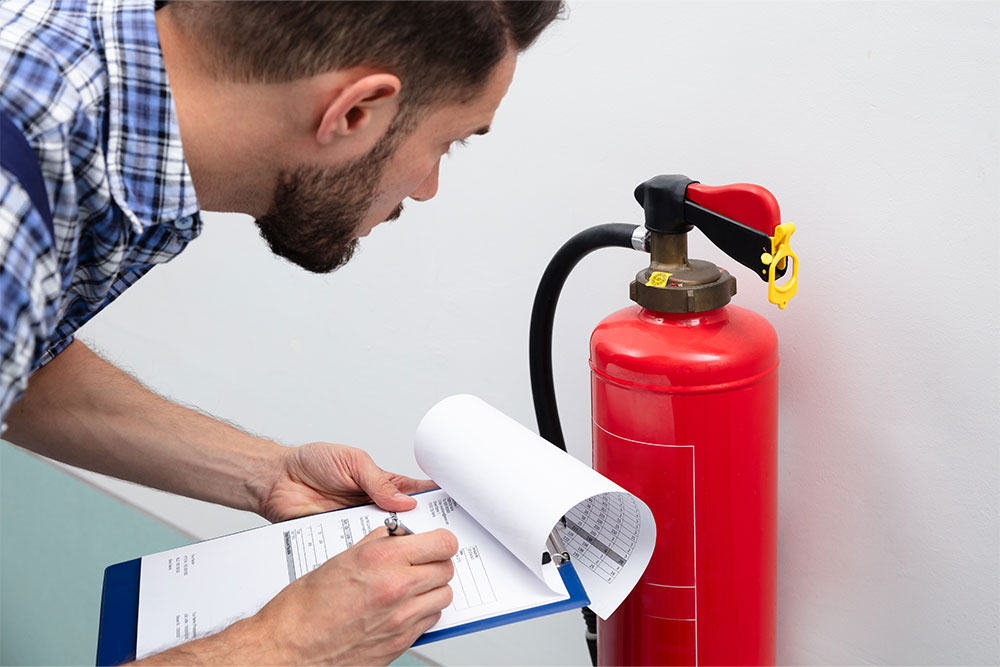
- Regular fire risk assessments are conducted in the workplace
- General fire precautions are in place
- A fire safety plan is in place
- Adequate fire safety training is provided to all staff
- Staff are kept informed of all fire risks in the workplace
- Staff are kept informed of all fire precautions in the workplace
The RRO places the duty on a ‘Responsible Person’ to ensure fire precautions are in place. The responsible person is: ‘the employer if the workplace is to any extent under his control.’
Suppose the workplace is not under the employer’s control. In that case, the responsible person can be a ‘person who has control of the premises,’ such as a manager, a landlord, an occupier, or a senior employee. It is sometimes the case that an employer will appoint more than one responsible person. Employers should note, however, that they are always legally held accountable for ensuring that fire safety in the workplace measures are implemented correctly.
The Fire Safety Responsibilities of Employees
If an employee is acting as a responsible person, they must ensure that sufficient fire precautions are in place and that fire safety policies and procedures are being followed. The responsible person can also conduct fire risk assessments and must ensure all firefighting equipment and fire prevention equipment is in good working order.
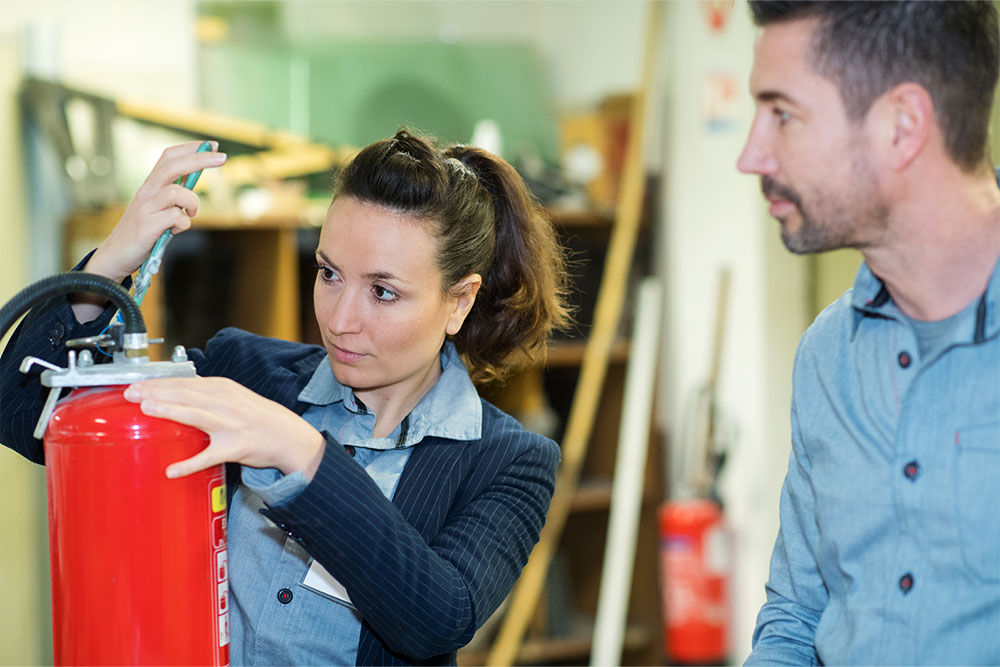

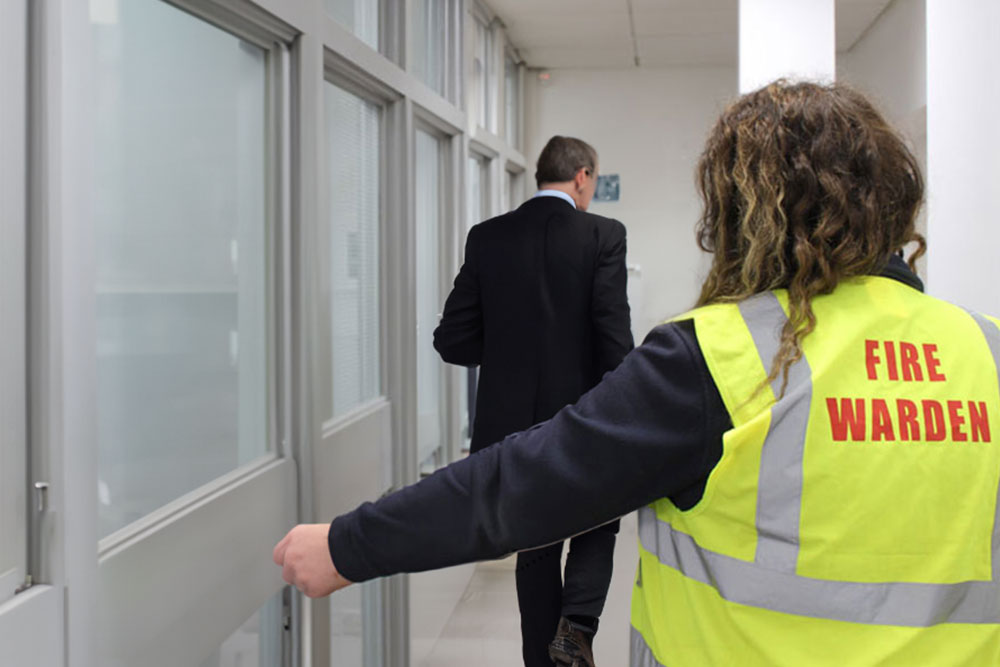
Employees must also be appointed specific fire safety roles. Under the RRO, every workplace must have at least one employee trained to act as a fire warden. A fire warden may also conduct fire risk assessments and maintain fire safety precautions, but they have additional responsibilities. Fire wardens must sound the alarm if a fire breaks out, provide aid to any injured people, act to stop the fire from spreading and manage the safe evacuation of the building.
In general, the RRO states that all employees must take reasonable care for their own safety and the safety of others. This means that employees must not act in a manner that puts themselves or others at risk. Employees must follow all fire safety procedures and participate in fire safety training. Suppose an employee becomes aware of a fire safety hazard or they have concerns about the business’s overall fire strategy. In that case, they must immediately inform a superior.
What if You are Found to Have Breached Health and Safety Legislation?
There are severe consequences for breaches of the RRO and the Health and Safety at Work etc. Act 1974. Breaching health and safety legislation is a criminal offence. The penalties can include fines of an unlimited amount or terms of imprisonment.
Breaches are usually investigated by the Health and Safety Executive (HSE) inspectors and tried in court. A recent example of a breach was the case of International Paint Limited in Gateshead. After an explosion caused an employee to suffer severe burns, the company was found guilty of breaching the Health and Safety at Work Act 1974 at the Newcastle upon Tyne Magistrates’ Court in November 2022. The court ordered the company to pay £800,000 in fines and £14,032 in costs.
How to Improve Fire Safety in the Workplace
An uncontrolled fire can put people’s lives at risk, destroy stock and reduce a building to ashes. A thriving business can be wiped out in just minutes. Providing your staff with fire safety training will ensure you comply with the law and give your people the skills to recognise fire risks, implement effective control measures and know what to do if a fire breaks out.
Our Fire Awareness Training can be taken online, so it’s easy to fit it around your work schedules. The course covers all aspects of fire safety in the workplace. It is approved by the International Institute of Risk & Safety Management.