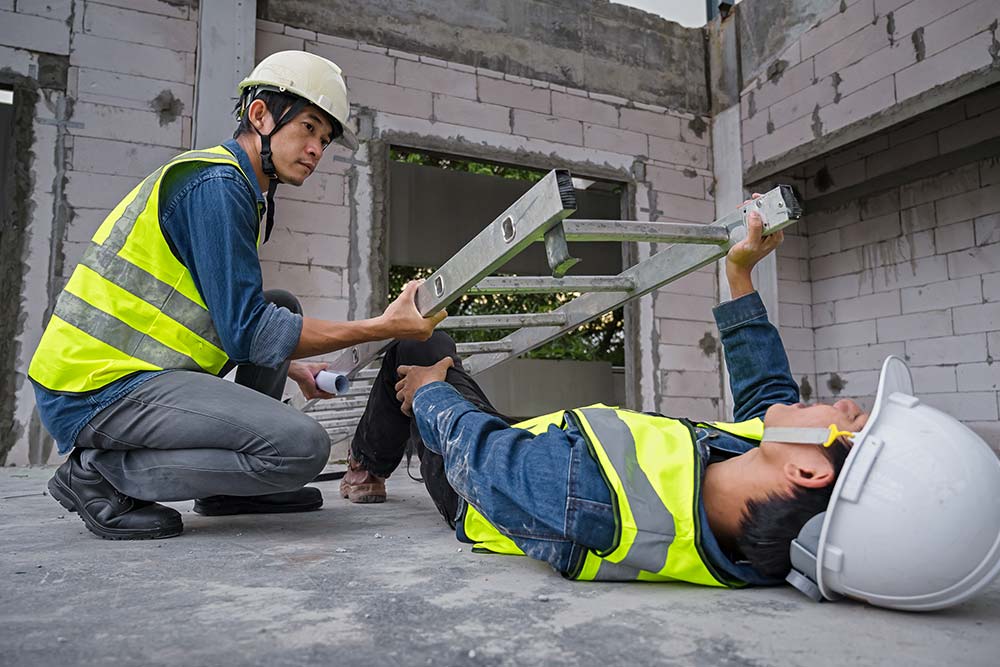
According to the most recent data from the Health and Safety Executive, falls from height accounted for more than a quarter of all workplace fatalities. A significant number of these incidents involved the incorrect use of ladders.
Taking simple, sensible precautions can not only reduce risks associated with ladder use, but also ensure you are meeting your legal duties. This guide will provide insight into ladder safety by highlighting the legal requirements, common hazards, and procedures necessary to prevent ladder-related accidents. As always, ensuring the provision of sufficient training, such as working at heights training online, remains a vital control.
What Does the Law Say?
Practising ladder safety is mandatory by law. It is the employer’s legal duty to ensure all risk assessments are accounted for as stipulated in section 6 of the Work at Height Regulations 2005. This law also includes guidelines specifically for ladders, stating how ladders must be set up, placed, secured, and used.
Employers and contractors must also refer to the requirements under the Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations (1999) (MHSWR), and Provision and Use of Work Equipment Regulations 1998 (PUWER 1998). These laws require employers to:
- Justify the use of ladders in their respective work sites
- Supply ladders that are suitable and well maintained
- Routinely inspect ladder equipment before use
- Inspect ladder equipment where circumstances change, such as any damage or modification done to the ladder
- Allocate a certified person for inspections
What Are the Main Hazards of Ladder Use?
If you are required to use a ladder at work, you must be aware of the hazards and dangers you are exposed to. The hazards that workers face when working on ladders include:
Poor Selection
Different ladders are designed for different types of work. It is important that the ladder you choose is correct for the task and can support the scope of work. This includes height, weight capacity, and equipment used during the task.
Failure to Inspect Ladders
Pre-use inspection is the cornerstone of ladder safety. Parts on the ladder can become worn or damaged over time. This can cause ladders to break, bend, or collapse when the worker is performing a task.
Ground Placement
To be stable, a ladder must be placed on solid ground. Sandy or dirty, damp, wet, or uneven ground placement will cause your ladder to slide out from under you.
Improper Set Up
Ladders don’t just need to be secure on the ground, they also need to be secure at the top. They need to be leaned against a solid surface and properly extended. If not, the ladder will remain at risk of being toppled.
Failure to Maintain Three Points of Contact
Three-point-contact means keeping two hands and one foot, or two feet and one hand on the ladder at all times during use. It may seem simple, but failing to maintain three-points of contact has led to uncountable accidents involving slipping off of a ladder or a loss of balance that results in a fall.
Overloading
Overloading the ladder can often lead to tipping or buckling. You must ensure that tools and materials added to the ladder’s weight do not exceed this limit.
Overreaching
Overreaching is a common cause of ladder-related accidents. This occurs when someone working on a ladder reaches too far away from the ladder, thereby compromising his/her balance and causing it to tip over.
Placement Near Other Objects
Placing the ladder near hazardous energy or objects can be extremely dangerous. This includes places where there is traffic, construction activity, or energised sources such as power cables.
Weather Conditions
Weather conditions pose a significant hazard to ladder safety. Rain, snow, excessive humidity, ice, and high winds can make the ladder slippery and unstable.
Lack of Suitable Equipment
It is highly important that proper gear is worn before mounting the ladder. Suitable footwear, gloves, safety helmet, and carabiners prevent slipping and fall in case of unforeseen circumstances.
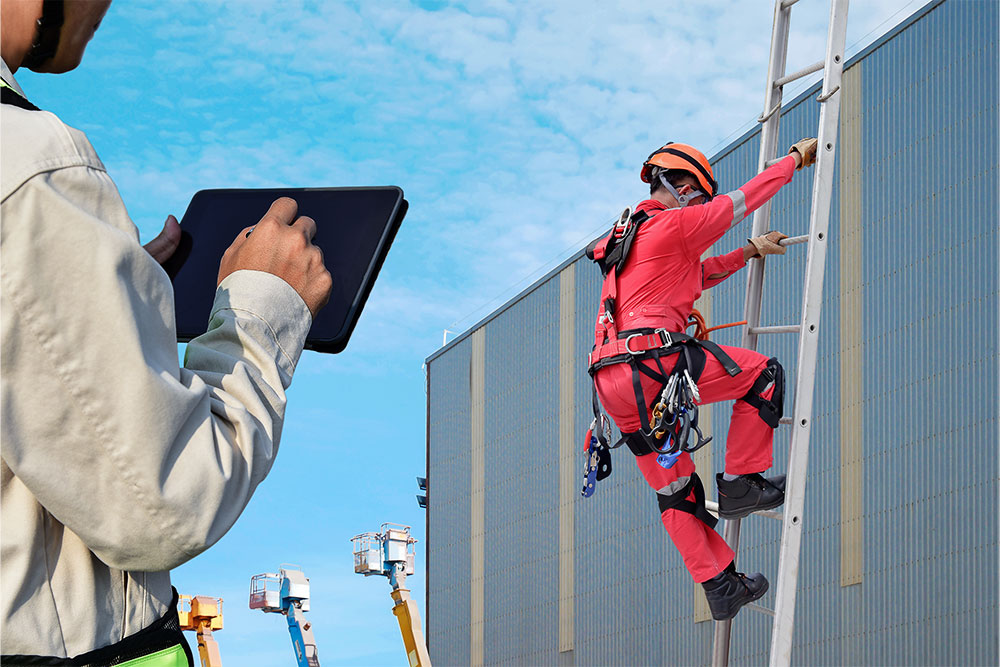
Lack of Training
Most importantly, all workers must have proper ladder safety training to ensure a safe work environment. Anyone using a ladder must understand how to complete a pre-use check every time the ladder is used.
Formal ladder inspections should also be carried out regularly and recorded. Anyone responsible for these inspections must be trained on how to do them properly. Online ladder safety training and working at heights training online is an excellent way to ensure this training is provided with records readily available upon completion.
Additional Hazards
Electricity
Electricity poses a hazard because the shock can harm you, but also cause you to fall. Shocks can occur by coming into contact with overhead power lines or when conducting work or repairs on or near a power source.
Vehicles &Pedestrians
Ladders set up near vehicles or pedestrians put the worker at potential risk of falling if the ladder is jolted or knocked over. You should also be aware of ladders set up near doors or windows that could be accidentally opened into the ladder.
Dropped Objects
Many accidents have occurred when somebody working up a ladder accidentally drops a tool or item down below. If someone is passing by, this can result in serious injury.
Pre-use Ladder Safety Checklist
Anyone who uses the ladder must be competent to identify, report, and control hazards. Employers are required to conduct risk assessment of the ladder to determine if the task is suitable and safe for their employees.
Some of the factors that should be considered when deciding if a ladder is right for the job, include:
- Stiles: Must be in good shape, with no cracks or splits
- Feet: Confirm the feet are not damaged, worn, missing
- Treads: Check the treads thoroughly for any signs of contamination or slipping hazards
- Hinge Joints: Make sure the hinge joints are not loose or missing screws
- Platform: The platform on the stepladder must not be buckled or bent
- Fixings: Confirm all fixings on the ladder frame are tightly in place
- Locking Bars: Check if locking bars are batten, worn or bent
- Hinges: Make sure the hinges functional, not corroded or worn
Safety Checklist During Use
- Length of Use: the ladder should only be used in one position for a maximum of 30 minutes
- Stable Platform: the ground and upper resting point of the ladder must be appropriate for stability
- Weight Limit: the person and equipment must not exceed the highest weight limit (BS EN 131 standard 150 Kg)
- Carrying Tools & Equipment: transporting tools and equipment weighing more than 10kg on a ladder should be avoided
- Safety Harness: a control measure such as a harness should be used if 3-point contact cannot be maintained
- Weather: avoid using the ladder if the weather conditions are not suitable such as rain, snow, or high-speed winds
- Warning Signs: use control measures such as warning signs when deploying ladders around pedestrian zones
Training Employees Is Your Legal Responsibility
Ladders are one of the most important and widely used tools on the job site. Ensuring proper safe work practices is crucial for protecting your employees from accidental injuries and possibly even death.
Human Focus’s Ladder Safety online training programme is designed to help strengthen the necessary skills your workers need to productively perform their tasks while remaining safe. The course covers all the essentials to ladder safety, risk assessments, inspection, and prevention in work environments.