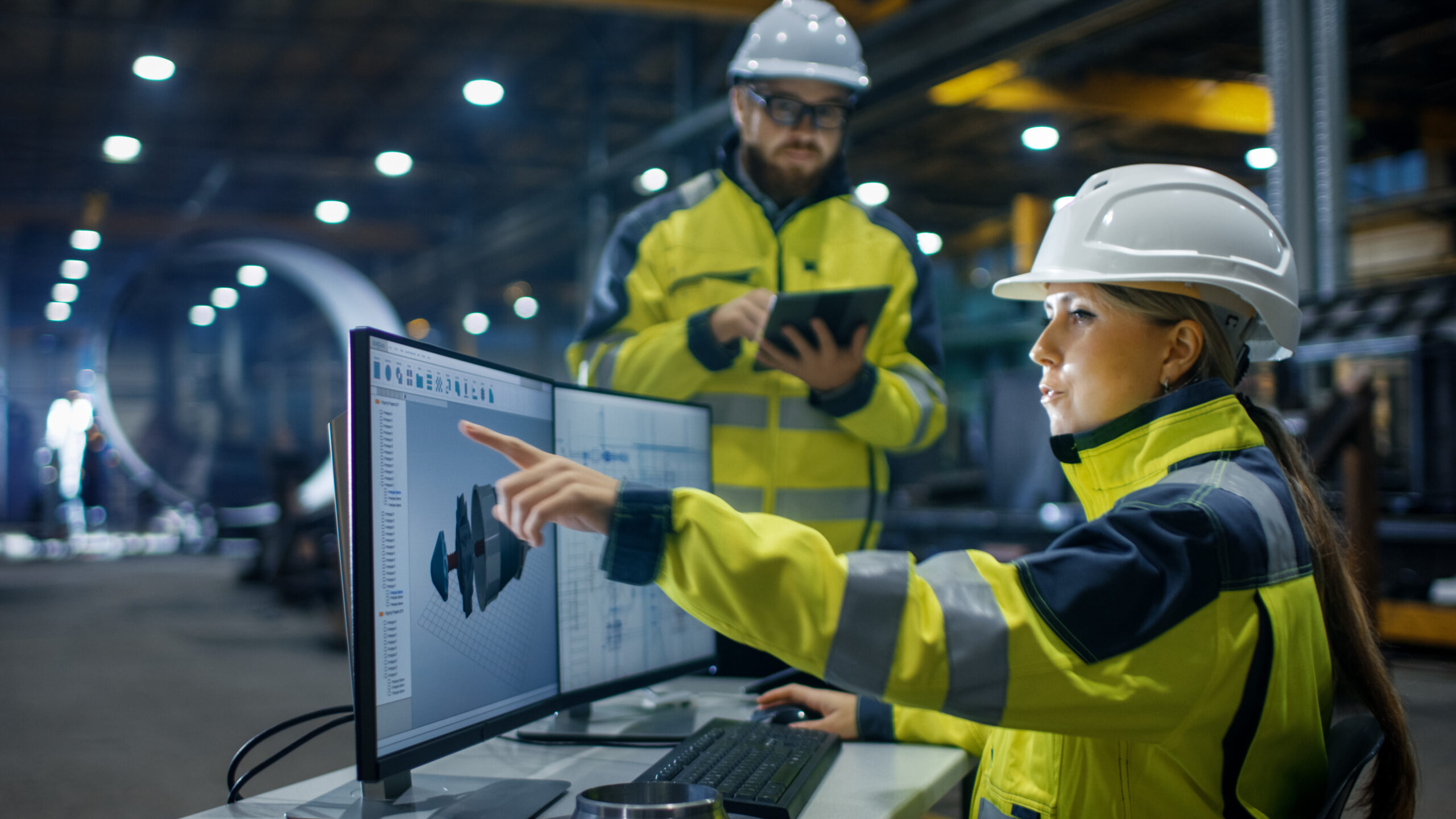
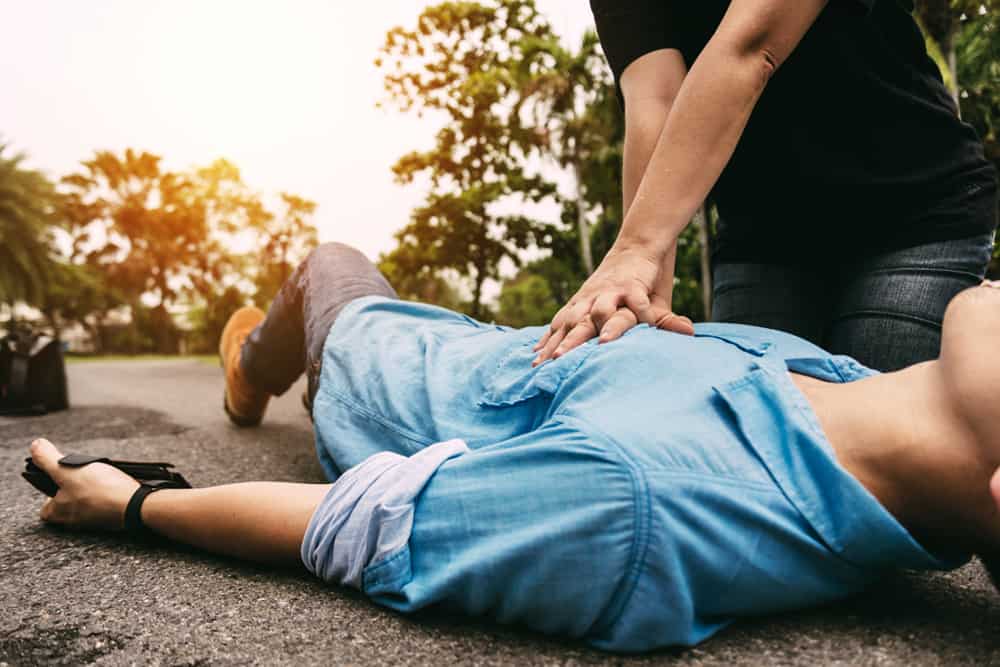
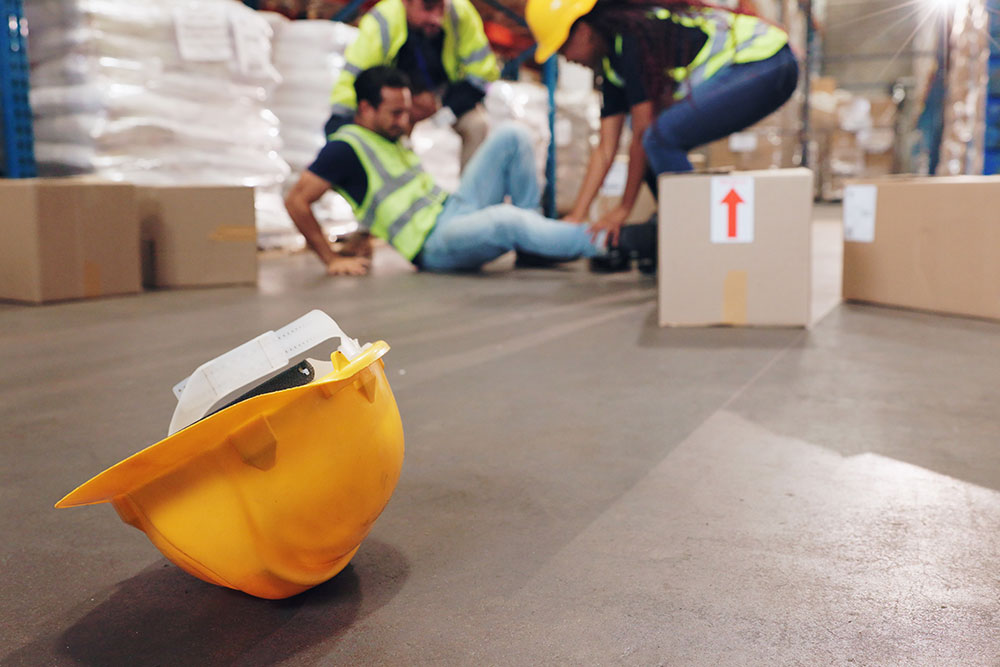
Regardless of what you do for work, understanding health and safety in the workplace is crucial for you. This blog delves into the critical question: Who is responsible for health and safety at work?
While it’s easy to point fingers or assume it’s solely the domain of health and safety officers, the reality is more collaborative and multi-faceted. From the top-tier management to the newest employee, each individual plays a key role in contributing to a safe working environment.
Whether you’re a business owner, a manager or a frontline worker, this blog will provide you insight into the layers of responsibility, legal obligations and practical steps to ensure safety and well-being at work. By the end, you’ll have a clearer understanding of your role and the collective effort needed to create a safe workspace, aligning with the UK’s stringent health and safety standards.
What is Health and Safety at Work?
Health and safety at work refer to the protocols, practices and measures implemented to ensure the well-being and security of employees in their workplace. This concept is not limited to the physical environment but also encompasses psychological and ergonomic aspects that can impact employees’ health and productivity.
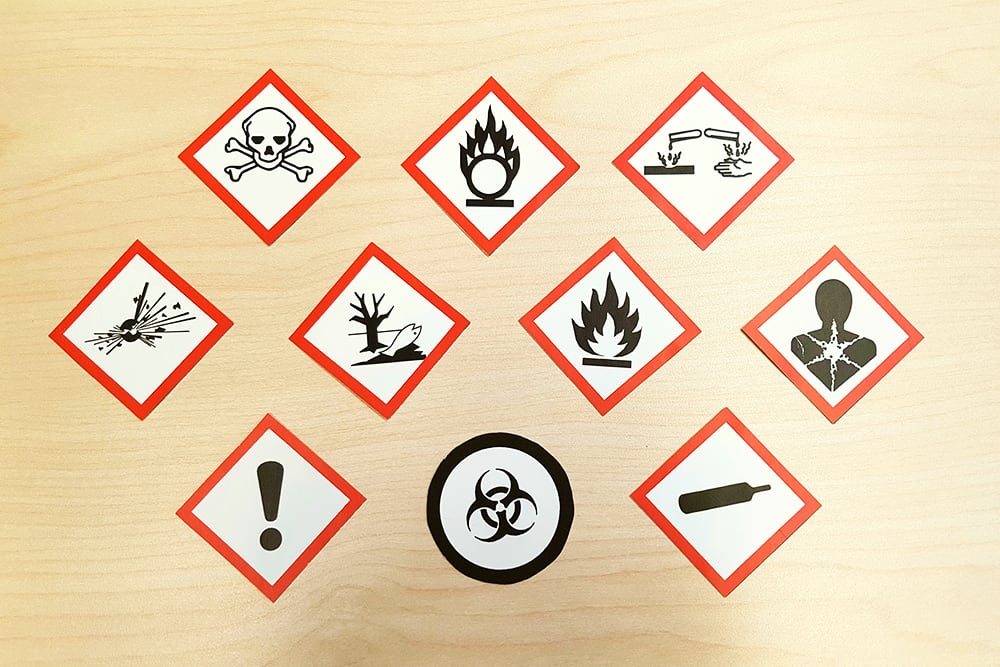
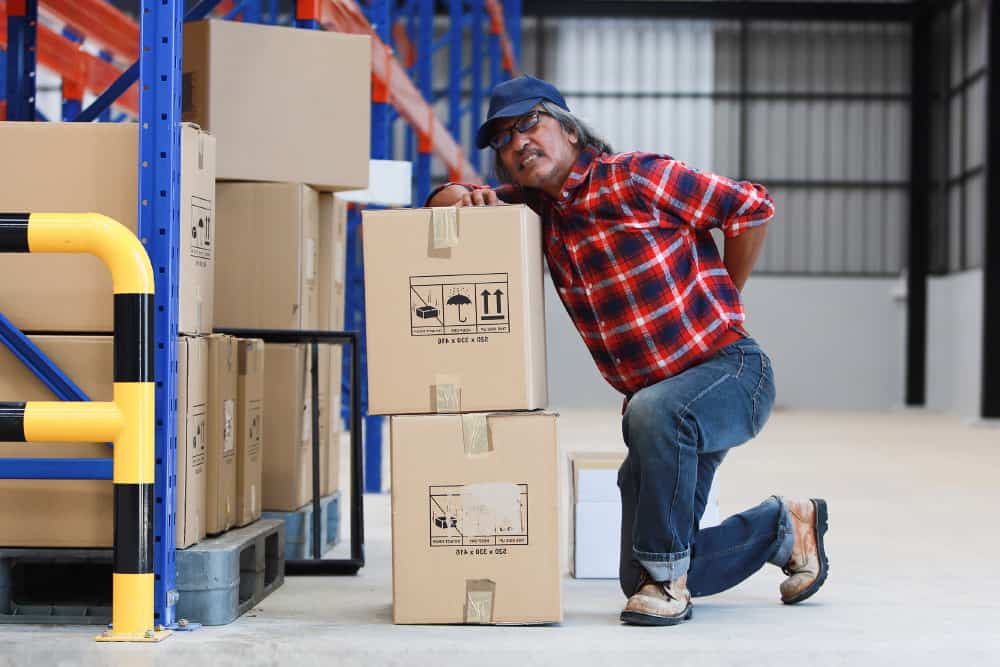
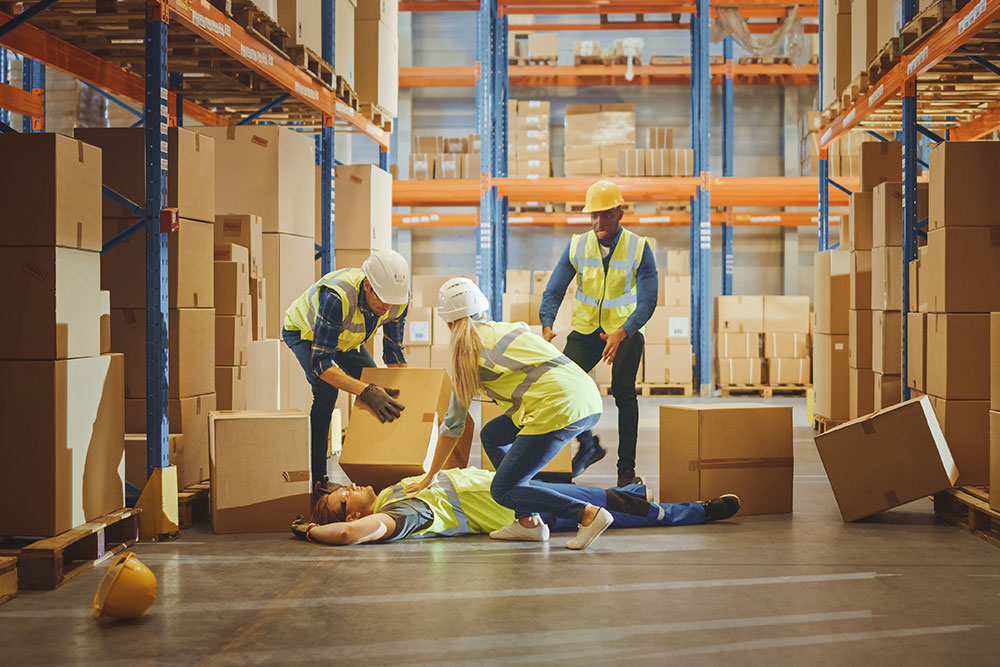
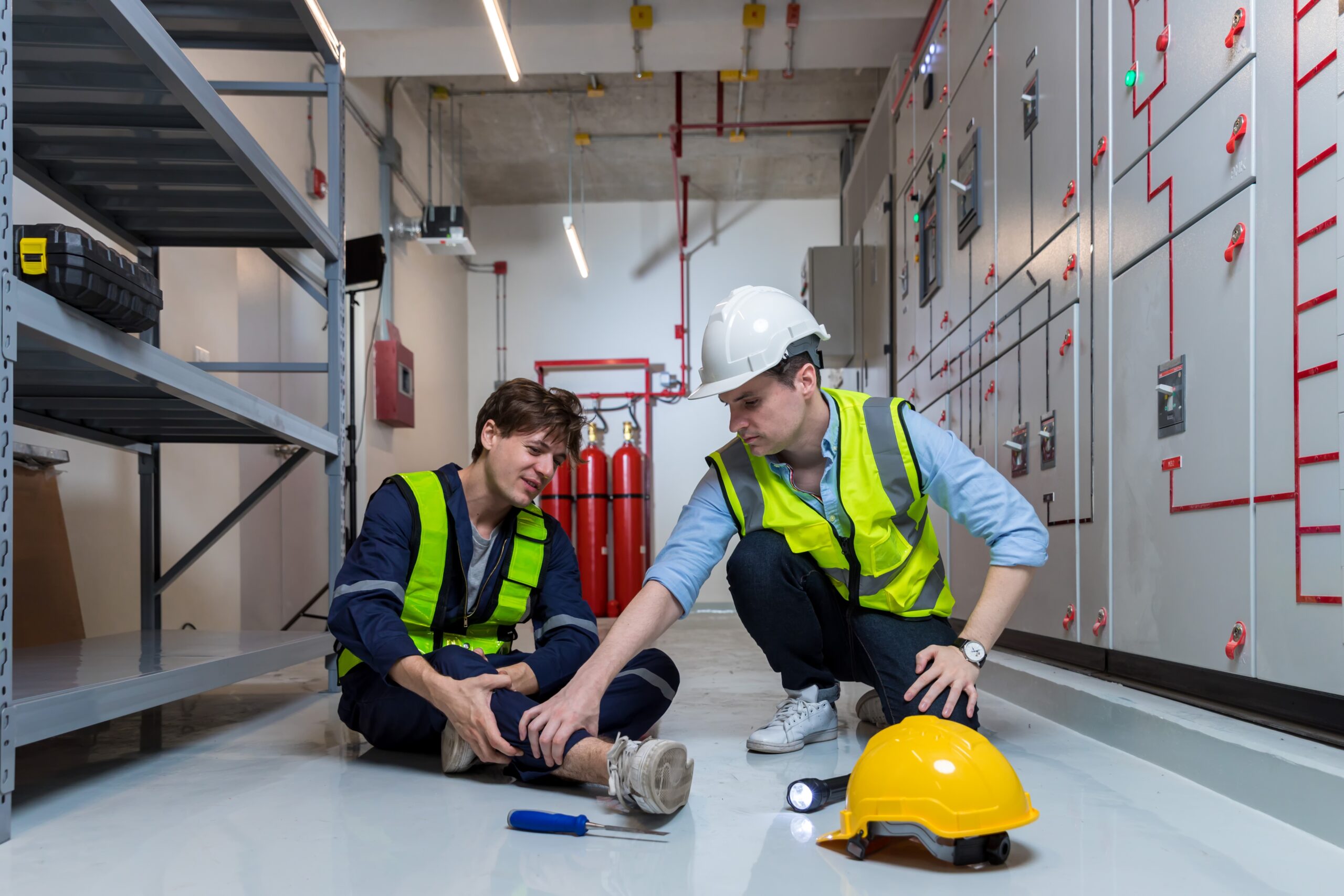
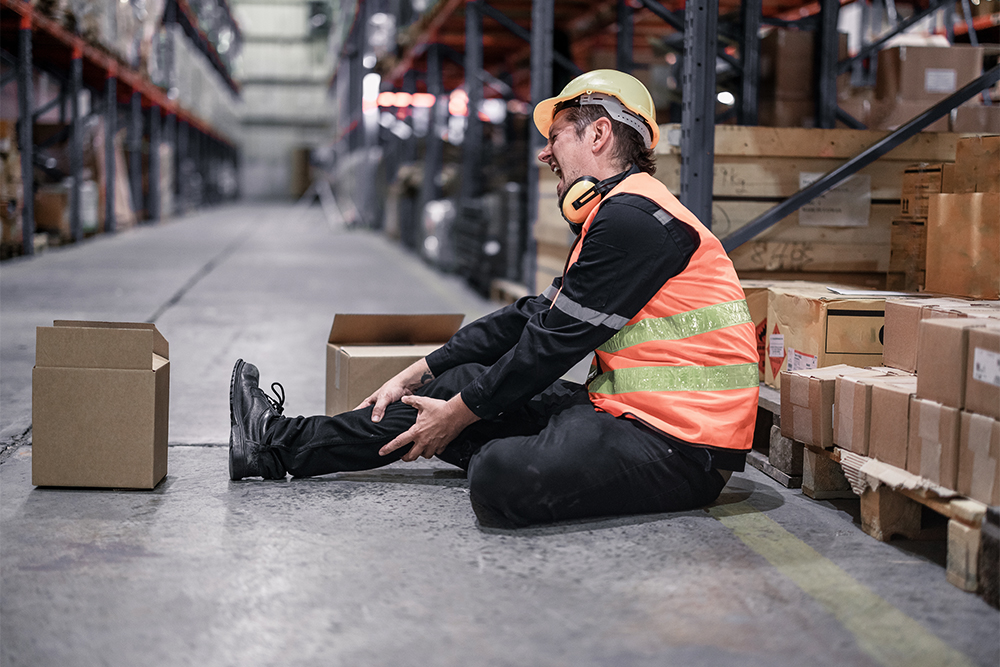
Every working environment has hazards inherent in the operations. Hazards are anything that can cause harm to employees or anyone else that may be affected. Harm can be in the form of physical injuries (a bump on the head), illness and disease (cancers caused by exposure) or psychological harm (stress and burnout). It can also take the form of worsening pre-existing conditions or fatalities.
Health and safety at work help minimise the likelihood of such hazards causing harm and the consequences if they do.
What is Occupational Health?
Closely linked to health and safety at work is occupational health. While health and safety at work is broader, and focuses on measures of preventing accidents and ensuring a safe work environment, occupational health focuses more on preventing health issues linked to work.
It includes several services such as health check-ups, keeping an eye on workers’ health, giving advice on illnesses caused by work and making sure the work environment promotes good health. These services might cover medical tests, watching health over time and offering support like counselling.
The UK Law on Health and Safety at Work
UK law emphasises health and safety at work through the Health and Safety at Work etc. Act 1974 (HASAWA). HASAWA is very broad: It sets out the general duties which employers have towards employees and members of the public, as well as the duties employees have to themselves and to each other.
This act is also an enabling piece of legislation, meaning it has laid the framework for numerous other laws that define more specific duties for controlling health and safety hazards. This includes the Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1999, which define requirements for employers to conduct risk assessments of workplace hazards.
It also includes more niche health and safety legislation, such as the Control of Substances Hazardous to Health (COSHH) 2002 regulations and the Provision and Use of Work Equipment Regulations (PUWER) 1998, which apply to hazardous substances and work equipment, respectively.
UK Employers' Health and Safety Obligations
Health and safety legislation sets out the fundamental duties employers have towards their employees and the public regarding health and safety. These responsibilities are crucial in ensuring a safe working environment. These include requirements to:
- Ensure the Health, Safety and Welfare of Employees: Employers must protect employees from potential harm by providing a safe working environment, equipment and systems of work
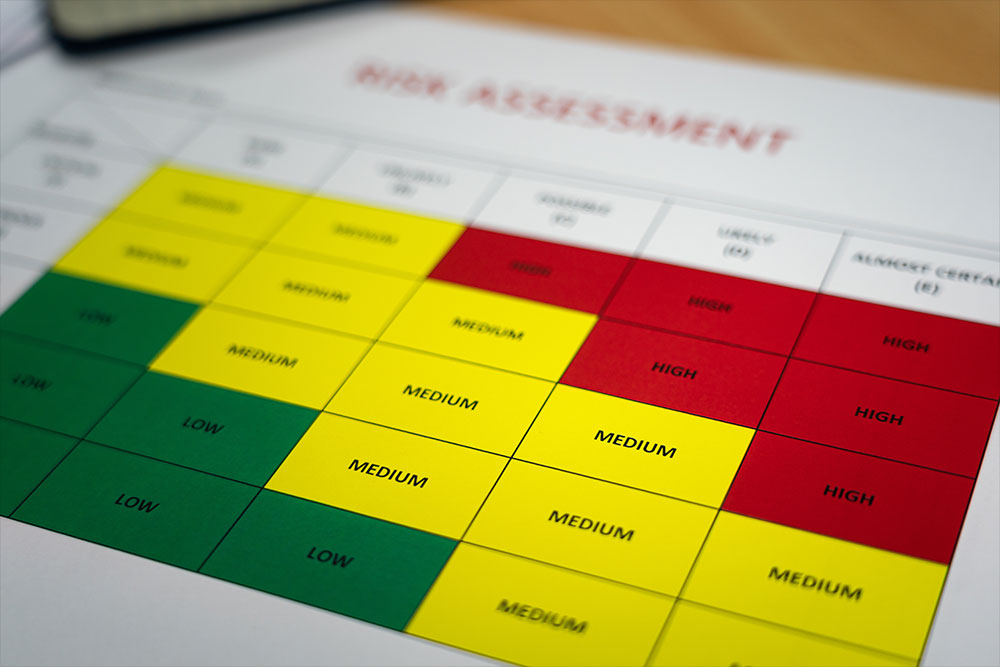
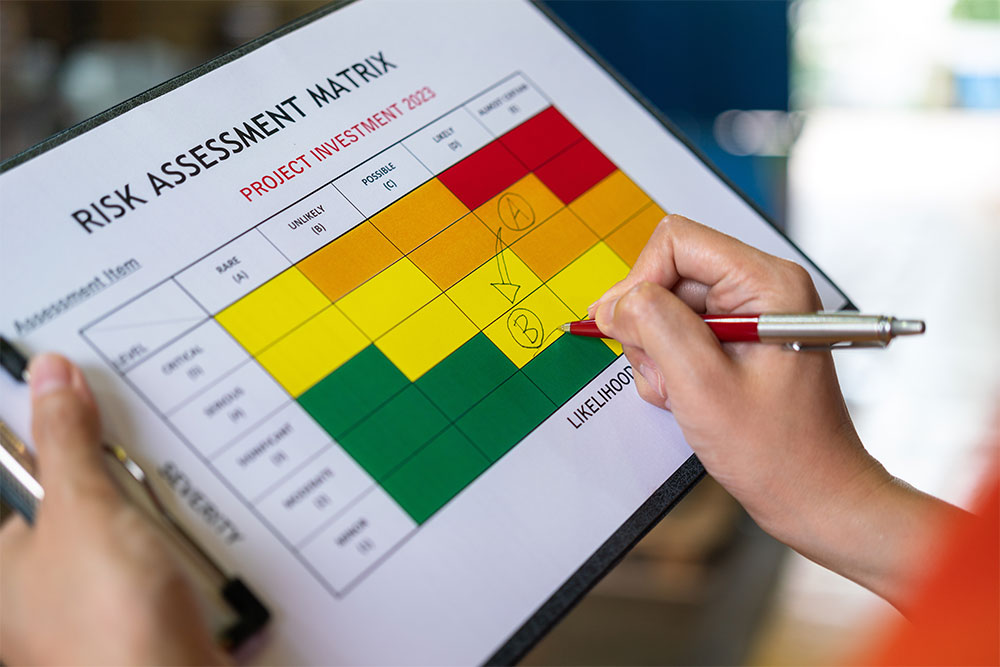
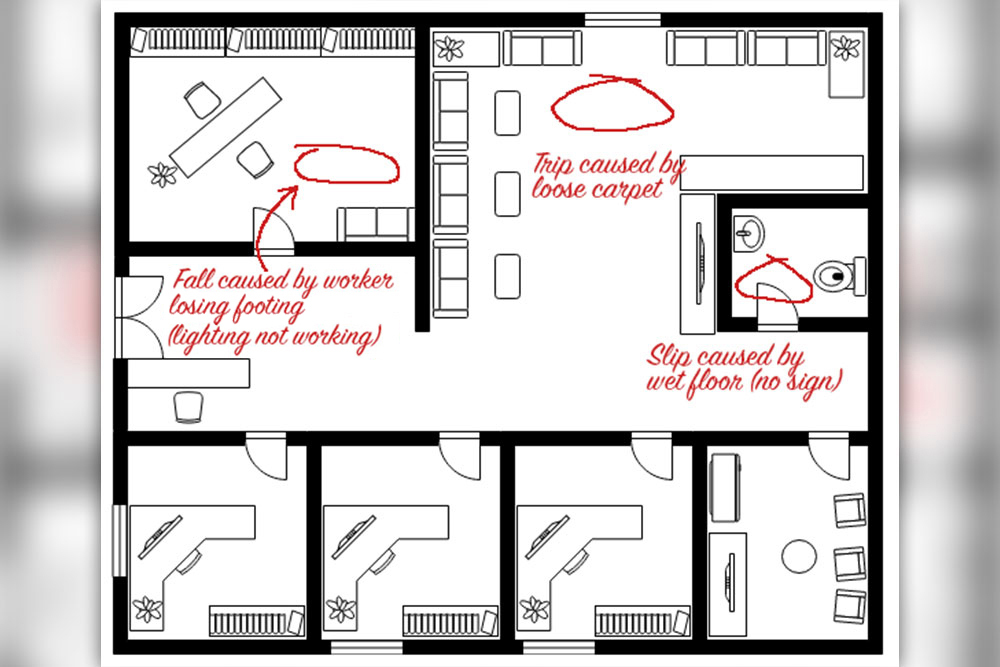
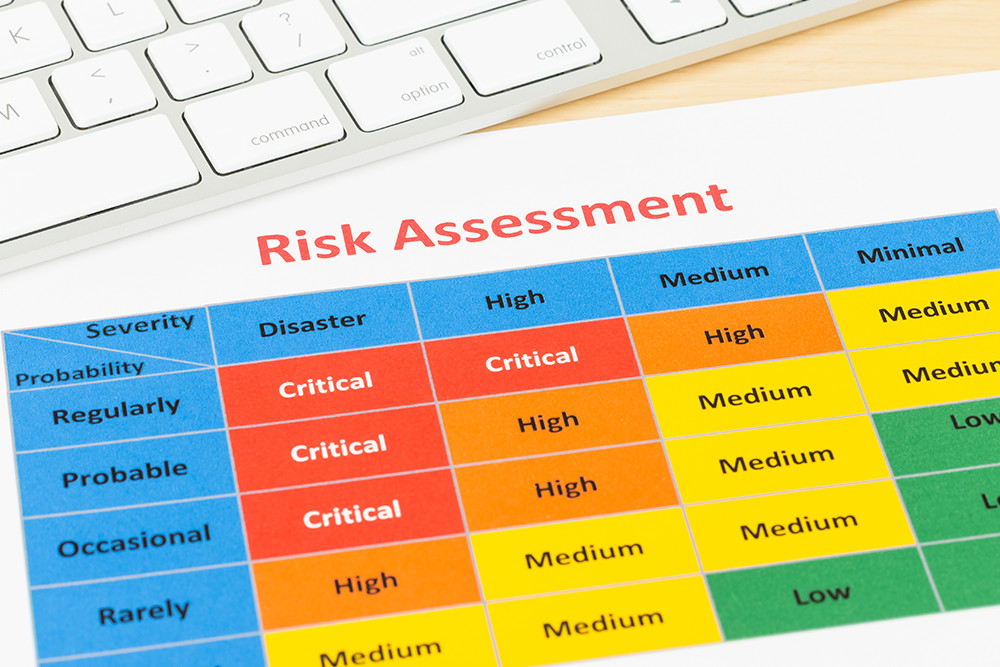
- Conduct Risk Assessments: Any ‘reasonably foreseeable’ workplace hazards must be risk assessed before work is conducted
- Reduce the Risk of Such Hazards: Hazards must be controlled to minimise the risk to a suitable level
- Provide Information, Instruction, Training and Supervision: Employers must ensure employees are well-informed and trained regarding their health and safety responsibilities
- Maintain Safe Work Conditions: This includes ensuring the workplace, machinery and equipment are maintained in a safe condition
- Facilitate Employee Welfare: Necessary facilities and arrangements must be in place to cater to employees’ welfare at work
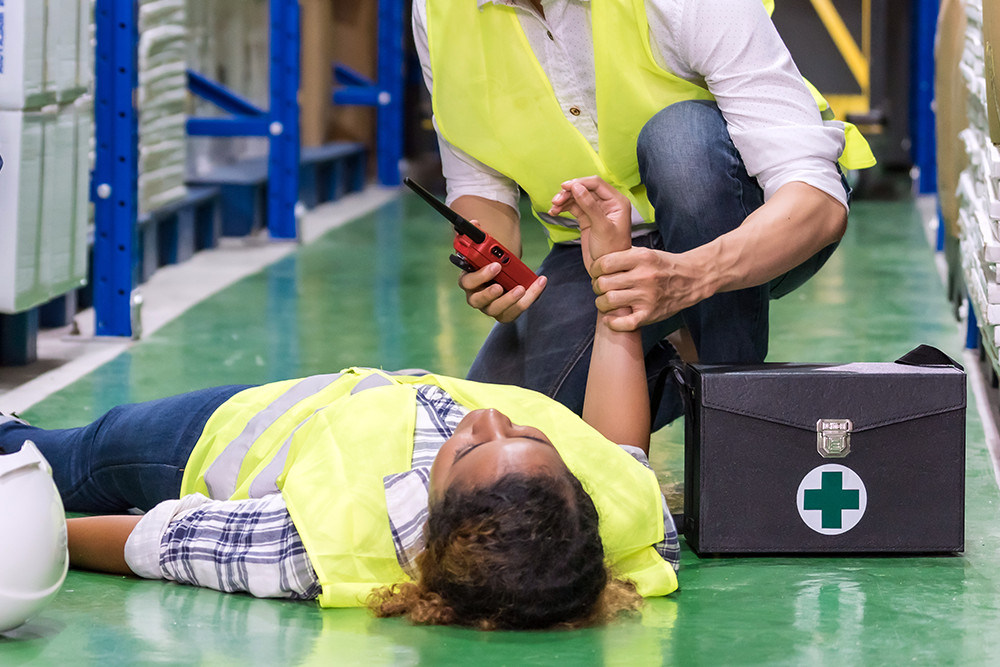
- Implement Emergency Procedures: Employers should have clear plans for emergencies, including evacuation procedures, and ensure employees are aware of these plans
- Engage with Employees on Health and Safety Issues: This includes consulting with employees or their representatives on health and safety matters affecting them

Employees’ Health and Safety Duties
Health and safety legislation also outlines specific duties that employees, and contractors or temporary workers, have to ensure their own safety and that of others in the workplace. These responsibilities are key to maintaining a safe working environment for everyone. Employees are required to:
- Follow Safety Procedures: Adhere to the safety policies and procedures established by the employer
- Use Safety Equipment: Properly use safety equipment and wear protective clothing when required
- Report Hazards: Notify employers of any potential hazards or risks they identify in the workplace
- Cooperate on Safety Matters: Collaborate with the employer on health and safety issues, following any training or instructions provided
- Avoid Misuse: Not misuse or interfere with anything provided for health, safety or welfare
- Participate in Training: Engage in training and education provided to enhance workplace safety
- Emergency Response: Understand and follow emergency procedures, contributing to a safe and orderly response to incidents
A Summary of the Main Health and Safety Obligations for UK Employers
To sum this up, if you are an employer in the UK, the main duty of ensuring your workplace is safe falls on you. Your job is to ensure that your operations are safe for employees, the public and anyone else that may be affected.
The law requires you to do so via a preventative approach – striving to prevent harm before it happens. For any workplace hazards present that are considered ‘reasonably foreseeable’ you must
- Assess the risks of such hazards
- Put control measures in place to minimise the likelihood of these hazards causing harm or the consequences if they do
However, employees, as well as contractors, also have a duty to work with you to ensure a safe workplace. Ultimately, a safe workplace is only created if everyone works together as a team.
Who Has Duties for Workplace Health and Safety?
Understanding and implementing health and safety practices in the workplace is not just a legal requirement but a fundamental aspect of maintaining a productive, secure and positive work environment.
Every member of the organisation, from management to the frontline workers, shares the responsibility of creating a safe space that aligns with the UK’s comprehensive health and safety regulations. By fostering a culture of safety, where everyone is aware of their roles and obligations, organisations can significantly reduce risks and contribute to the overall well-being and success of their workforce.
To further enhance your knowledge and ensure your business remains compliant with the latest health and safety standards, consider enrolling in our range of online Health and Safety Courses. These courses are designed to equip you and your team with the essential skills and insights needed to navigate the complexities of workplace safety effectively.