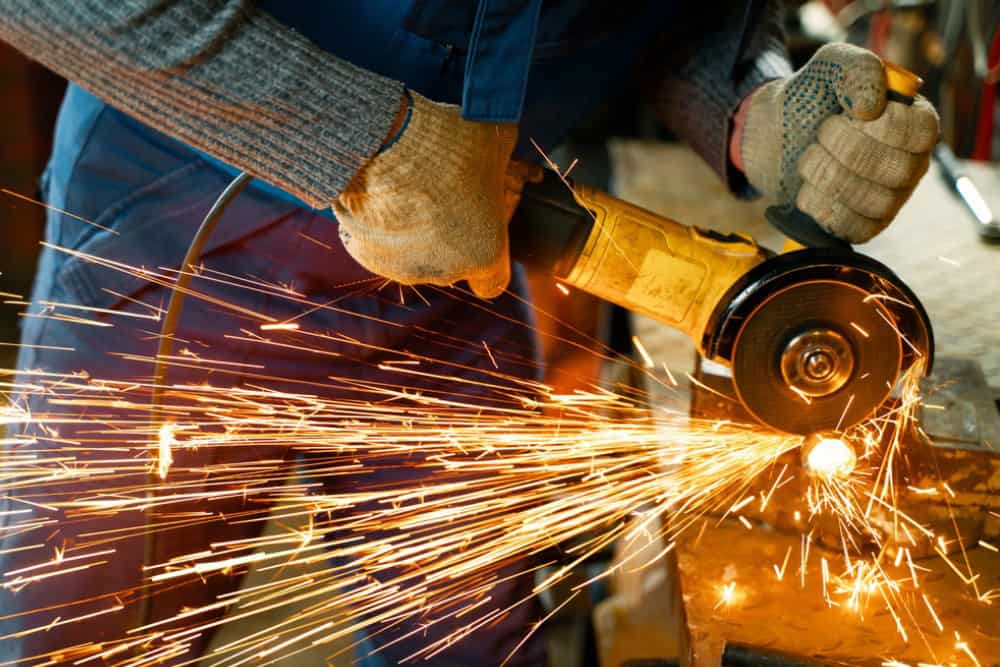
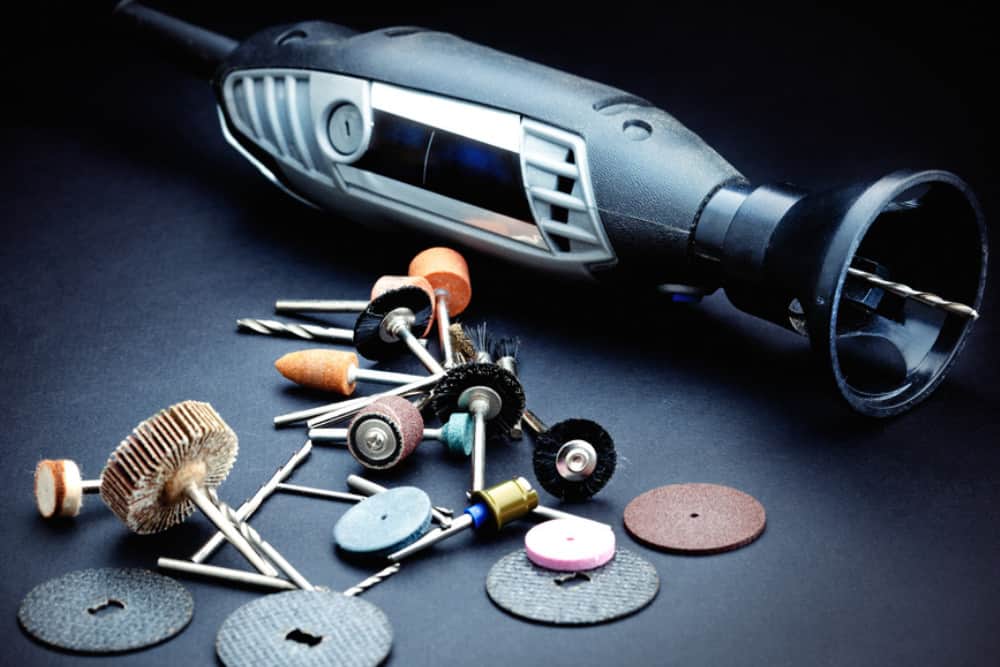
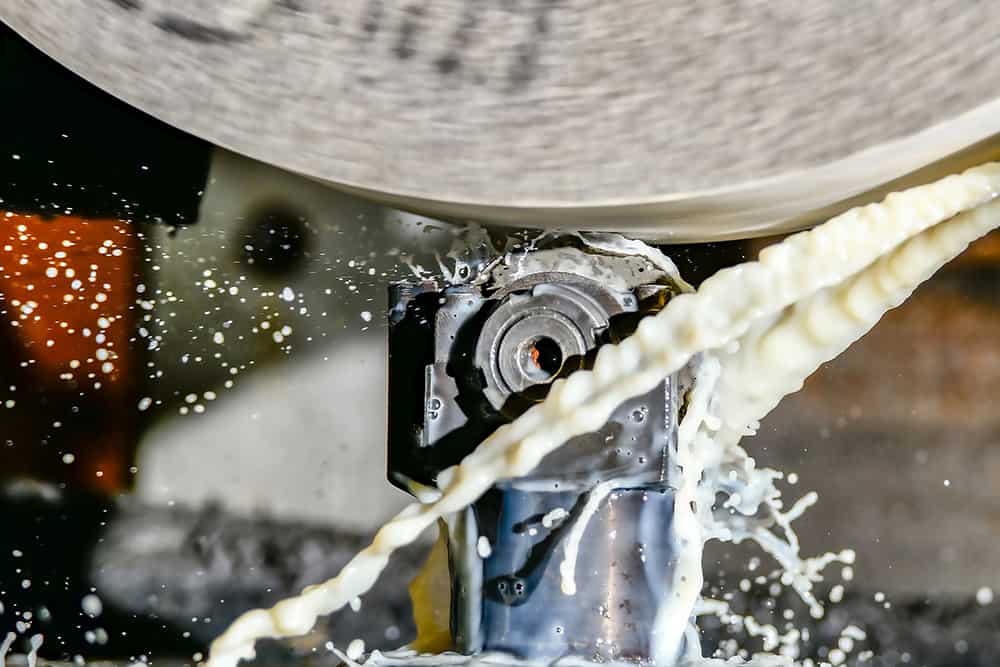
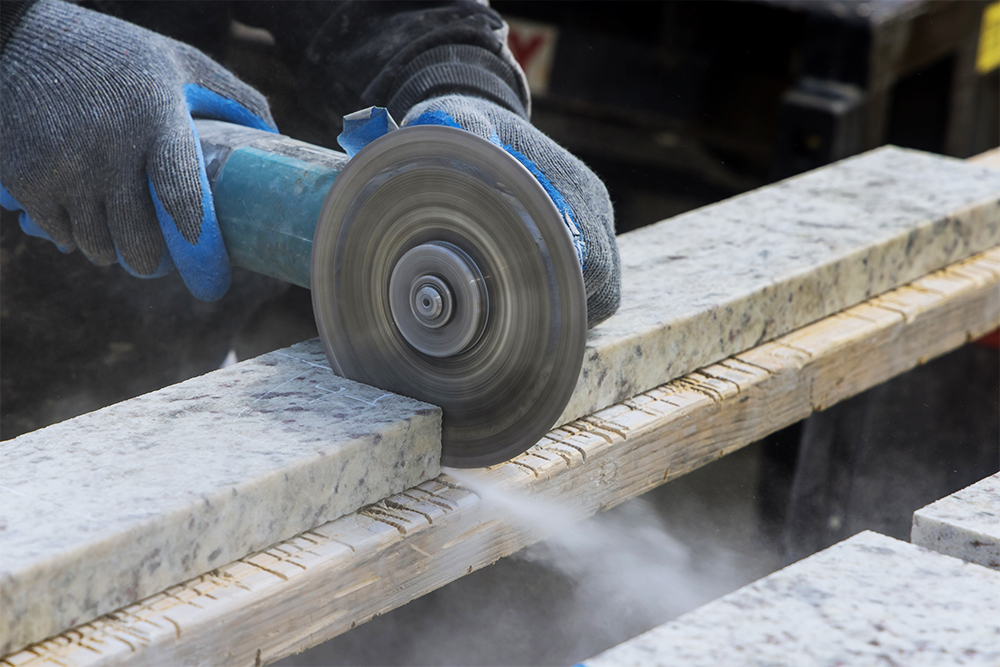
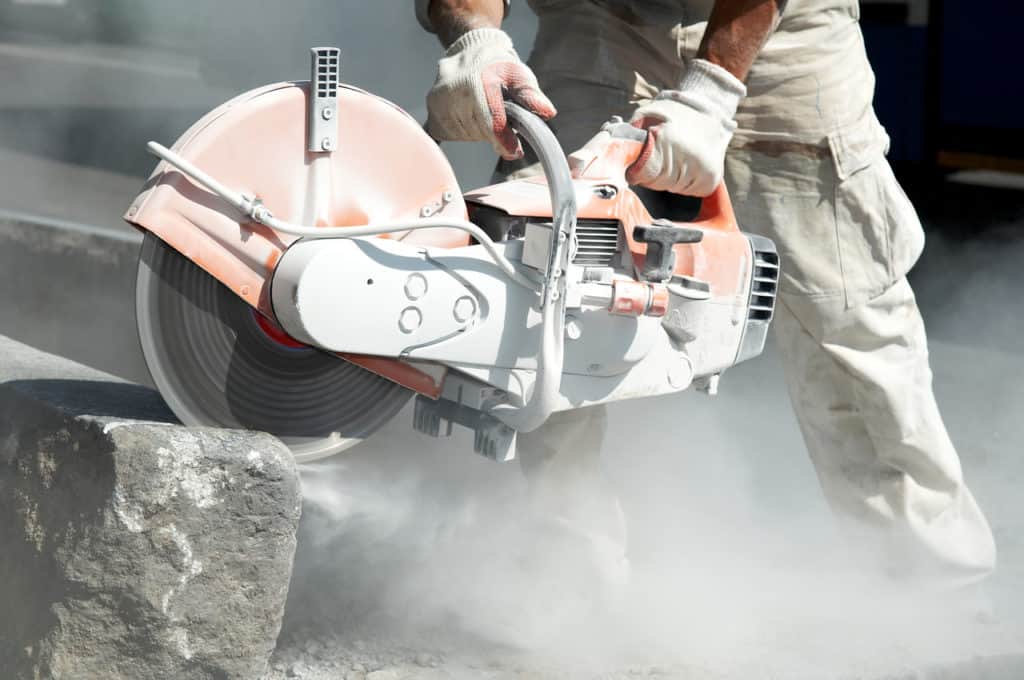
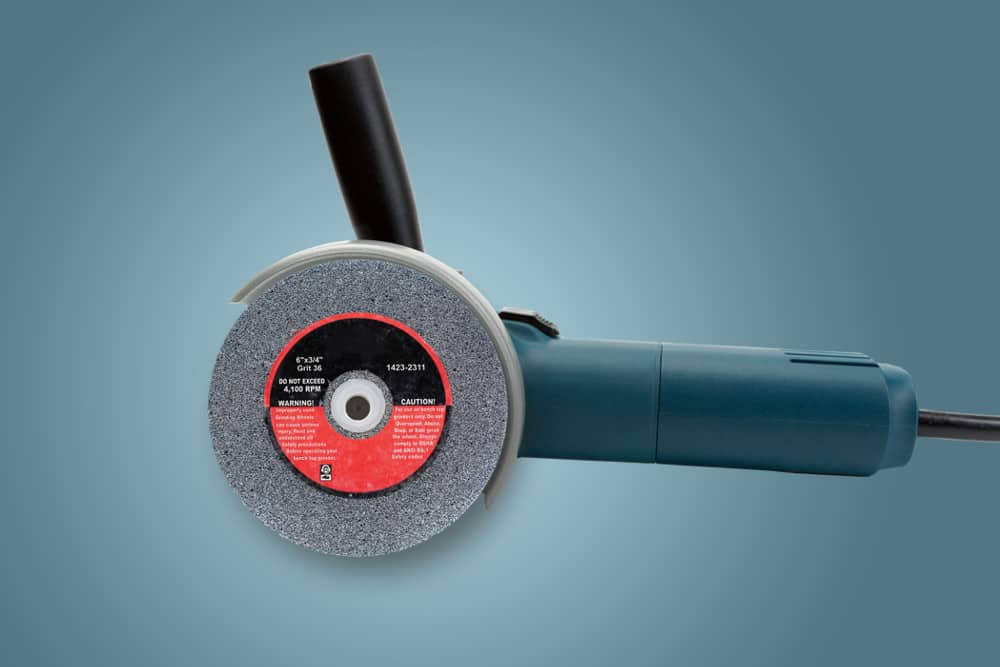
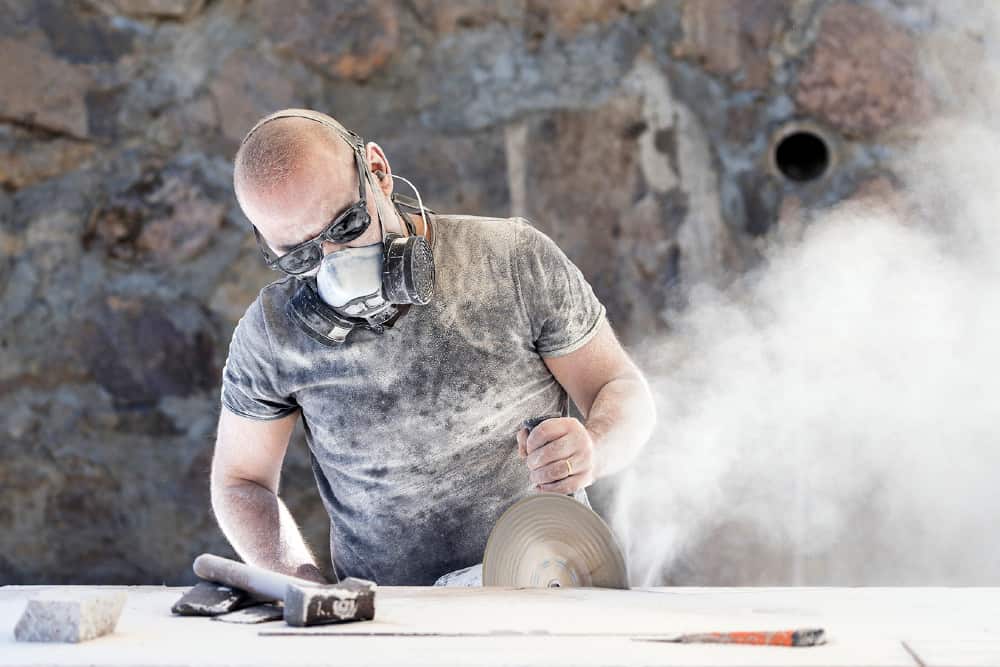
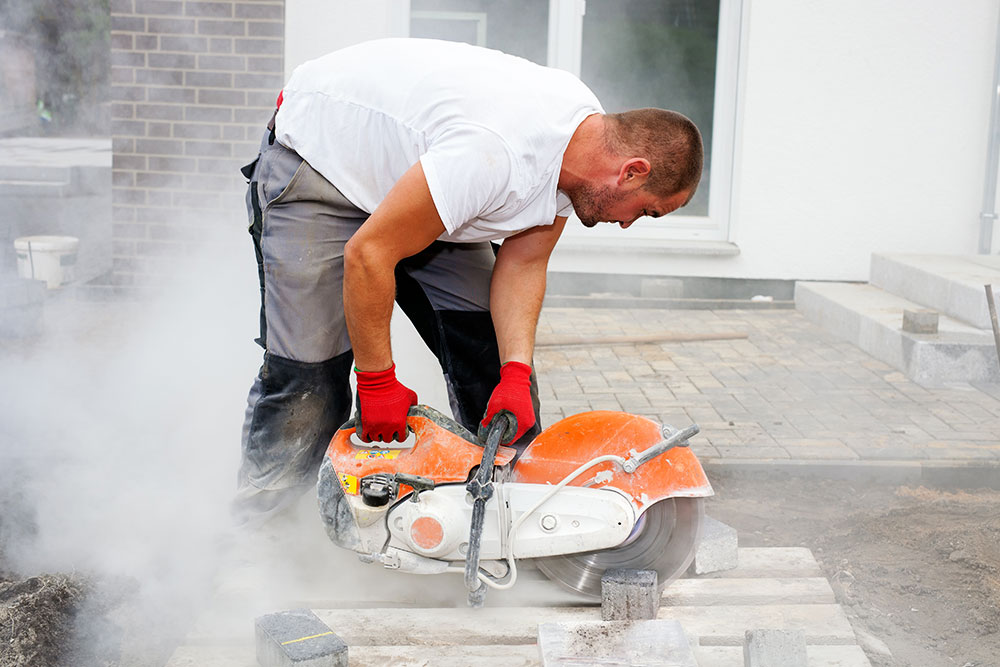
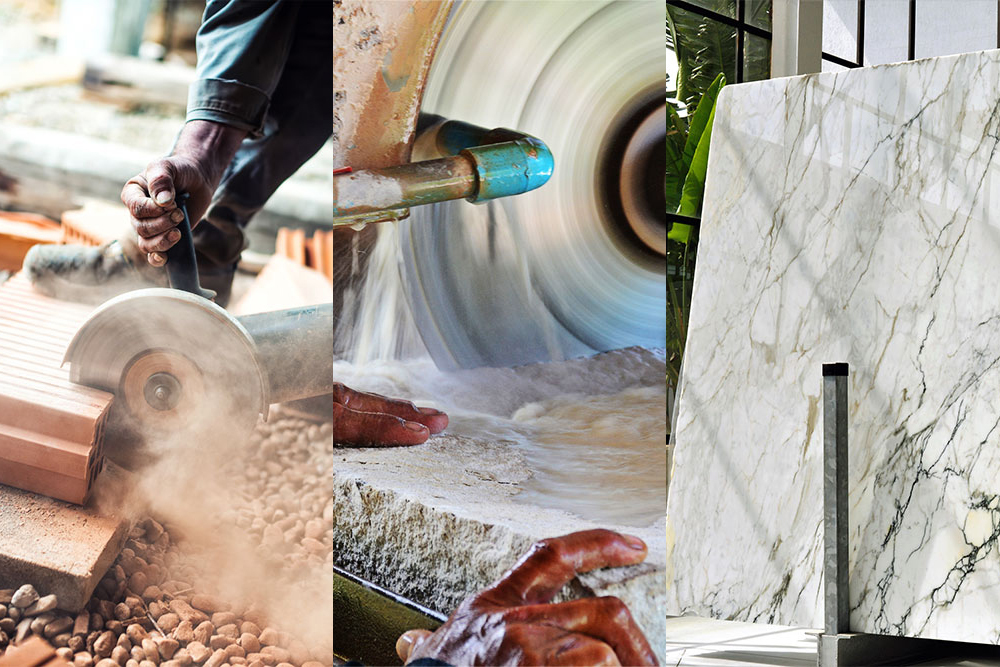
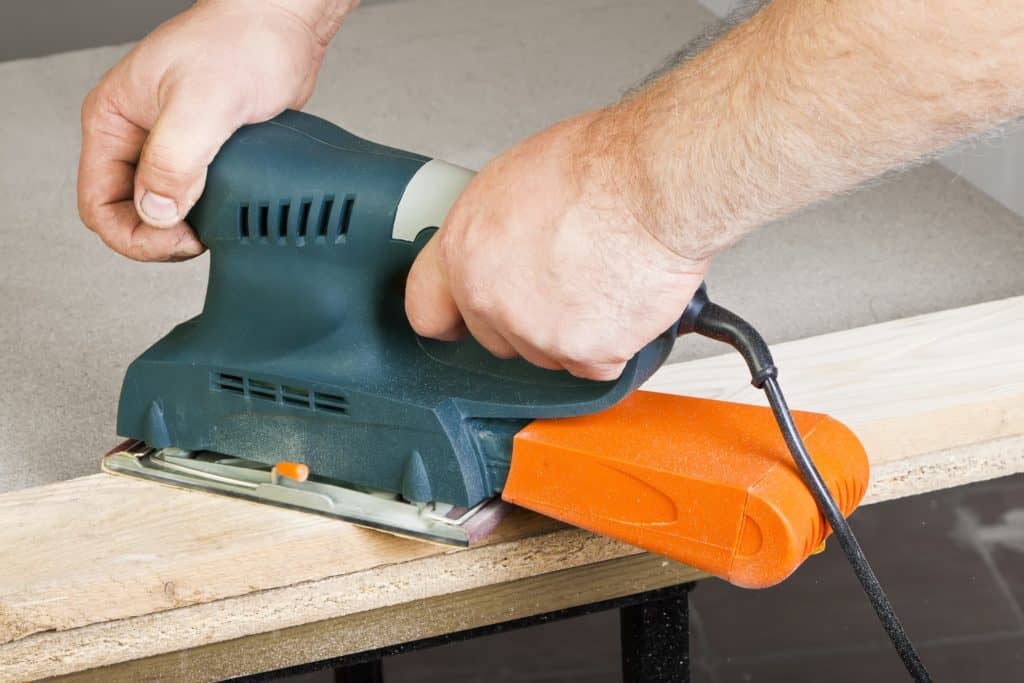
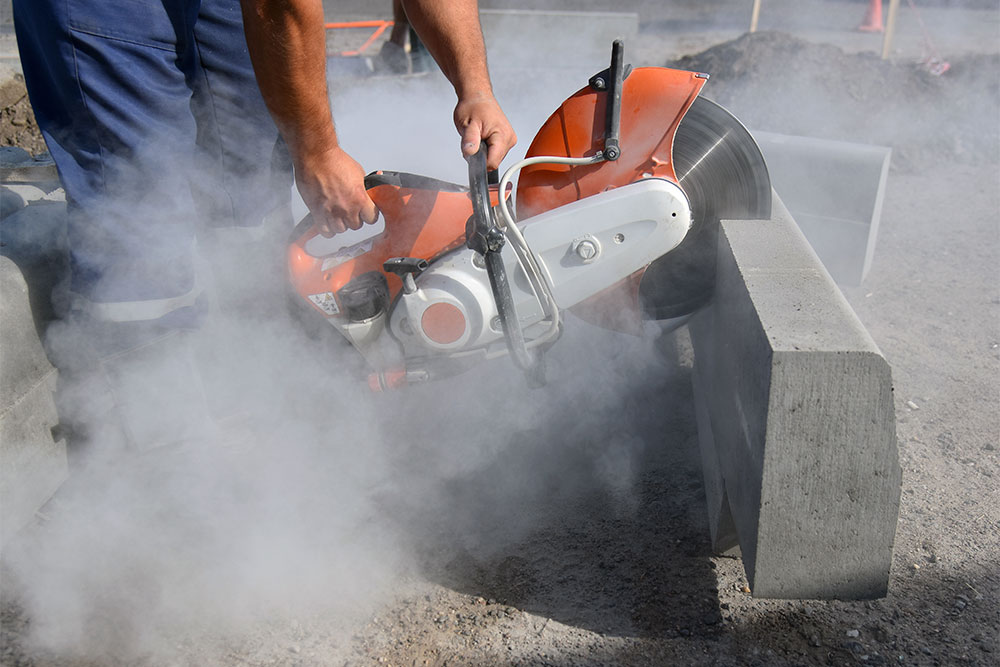
Abrasive wheels are commonly found in workshops and industrial factories throughout the UK. They are typically used in angle grinders but can also be found in a wide variety of tools and equipment. They are highly efficient at shaping, cutting and grinding hard materials like tile and metal.
However, when used incorrectly an abrasive wheel can cause severe injuries. Approximately half of all accidents involving them are caused by either operator error or unsafe work practices, according to the Health and Safety Executive (HSE).
Anyone using abrasive wheels must thoroughly understand what they are and how to safely use them.
This article provides you with a description of what constitutes an abrasive wheel, the types of abrasive wheels and what markings can be found. We will also look at the hazards of using them and show you where to find its training.
What Is an Abrasive Wheel?
An abrasive wheel is defined, by the HSE, as a “wheel consisting of abrasive particles bonded together with various substances”. They are disposable tools that can be manufactured in wheel shapes or as cups or cones. They are used for cutting and grinding hard materials as well as for polishing, sanding and deburring purposes.
The abrasive particles are usually grit-like materials bonded by either inorganic substances like glues or organic substances such as resin. Organically bonded wheels are generally found in handheld tools and portable machines. Inorganically bonded wheels are used in larger machinery and equipment.
The Different Types of Abrasive Wheels
The most common types of abrasive wheels are:
- Straight wheels
- Cylinder wheels
- Tapered wheels
- Straight cup wheels
- Dish wheels
- Saucer wheels
Types of Wheels – Characteristics
The various types of wheels have differing characteristics, which include:
- Size of the grit
- Type of binding substance
- Abrasive material used
- Grade of the wheel
- Shape of the wheel
The grade of abrasive materials, grain spacing, and volume of abrasive materials depend on the structure. Abrasive wheels with softer grit are used for sanding, polishing, grinding, or cutting of hard or soft materials.

What to Consider When Choosing an Abrasive Wheel
Under the Provision and Use of Work Equipment Regulations Act (PUWER) 1998, it’s the employer’s duty to make sure that any wheels used for work purposes are used as intended and fit for purpose.
The Supply of Machinery (Safety) Regulations (SMSR) 2008 place a legal duty on manufacturers to ensure any abrasive wheels they supply are safe for use and specified. A certificate of conformity must be supplied along with the abrasive wheel, a CE marking or equivalent UKCA or UKNI marking affixed and operating instructions and information must be supplied. So, when selecting a wheel it is essential to check this information.
Factors to consider include:
- Spindle speed of the machine being used
- Type of surface to be worked on (stone, metal, wood, etc)
- Contact area size, between the wheel and the material
- Type of machine being used
- Condition of the machine
The Hazards of Using Abrasive Wheels
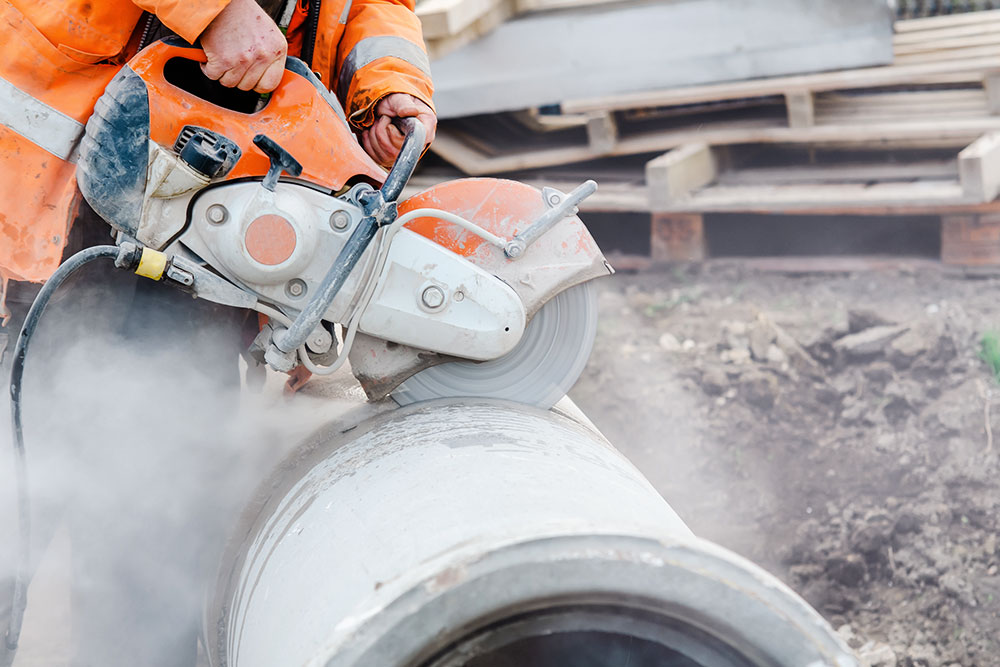
When in use, an abrasive wheel spins at very high speeds and emits large amounts of debris. It is essential to remember that they are potentially extremely hazardous and must be used with care.
Accidents involving abrasive wheel equipment are extremely common. Usually, these incidents are caused by a failure to follow abrasive wheel safety procedures.
Some of The Most Common Risks When Using an Abrasive Wheel Are:
- Drawing in hazards – for example, loose clothing or jewellery that can catch on to moving parts
- Impact injuries – as the result of flying debris or pieces from a damaged or defective wheel. The workpiece itself can also shift or be ejected
- Cuts and abrasions from direct contact – typically, these occur because of unintended slips or sudden movement
Abrasive Wheels Safety Tips
Tips for the safe use of abrasive wheels are to:
- Contain Drawing in Hazards – do not wear loose clothing or jewellery, and keep it and any hair away from moving parts
- Wear PPE – appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as face protection, gloves and safety shoes must be worn
- Protect the Area – your work area must be cordoned off to ensure that flying debris cannot strike anyone
- Maintain Good Housekeeping – keep your work area clean and well lit. Keep the handle areas dry, clean and free from oil and grease
- Avoid Slipping and Tripping Hazards – make sure you work in a stable or balanced position
- Don’t overreach
- Don’t Work Unless 100% – never use an abrasive wheel while you are tired or under the influence of drugs, alcohol or medication
- Use Auxiliary Handles – (if fitted) for maximum control over the torque reaction or kickback
- Avoid Wheel Breakage – Use wheels only as instructed by the manufacturer. Ensure that the wheel used is rated for the speed of the tool and that the correct type of abrasive product is used
- Inspect Your Wheels – Ensure that the wheel is in good condition before starting work
Where to Find Abrasive Wheel Training
Abrasive wheels are commonplace in workplaces throughout the UK. These tools can be extremely hazardous, even when operated correctly. Anyone whose job requires them to operate an abrasive wheel should know how to set it up correctly, operate it and maintain it.
In order to be able to use an abrasive wheel safely, specialised training should be undertaken by the operator.
Human Focus offers an accredited online abrasive wheels safety course that gives participants the knowledge to minimise the risk of injuries. By providing employees with abrasive wheels safety training, employers can keep their workplaces safe, protect the health of their staff and ensure that the workplace fully complies with all relevant UK health and safety legislation.