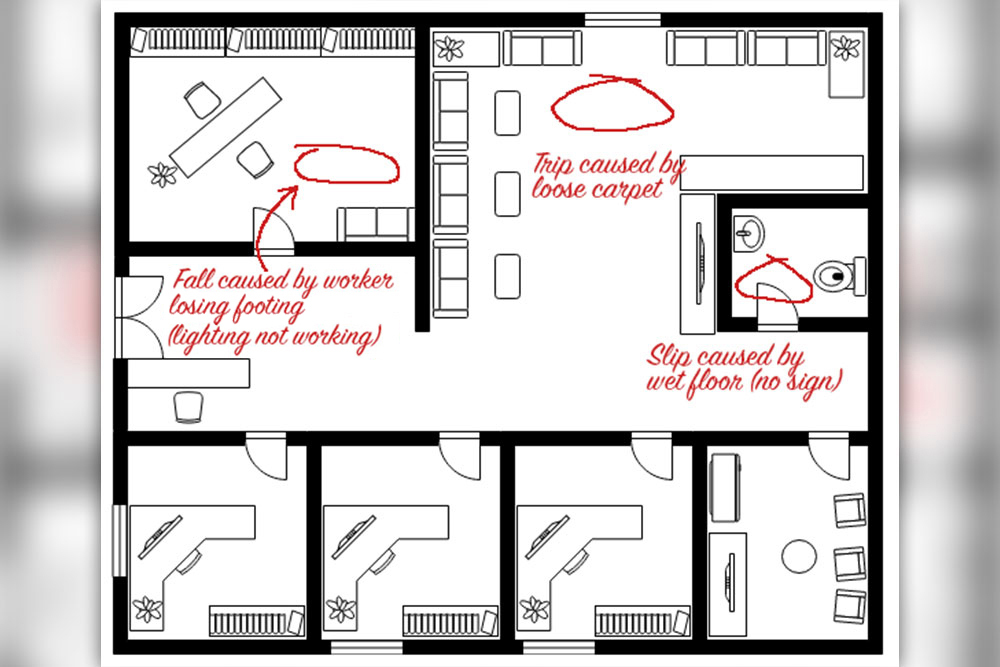
Employers have a duty of care to their employees and anyone else on their premises. By law, work activities must not harm those who carry them out or are present as they happen.
There’s no single way to meet this duty. Health and safety law is flexible, because those who create risks are best placed to manage them.
To help duty holders, the International Standards Organisation developed ISO 45001 – its standard on occupational health and safety management.
This guide explores the standard’s principles and how implementing them can improve safety and compliance in your workplace.
Key Takeaways
- ISO 45001 provides a structured framework for managing occupational health and safety and reducing workplace risks.
- Improving workplace safety can enhance productivity, reduce costs, and strengthen market positioning.
- Certification is optional, but implementing ISO 45001 can still enhance safety performance.
What is ISO 45001?
ISO 45001 is a framework for occupational health and safety (OHS) management systems. It’s one of the many standards developed by the International Standardization Organization (ISO).
ISO produces internationally recognised standards covering almost all areas of business technology, manufacturing, and management.
If you want to ensure health and safety in your workplace, ISO 45001 can help. It provides a framework for identifying and controlling every factor in your workplace that might cause harm, from physical hazards to human behaviour.
What Are the Key Principles of ISO 45001?
Like all ISO standards, ISO 45001 is built on extensive research and expert knowledge. Fully implementing its framework should produce the best possible occupational health and safety management system for your organisation.
These world-class systems are founded on three core concepts:
- Processes must be documented to ensure clarity and consistency in safety protocols
- Hazards must be proactively identified and managed to prevent harm
- Safety systems must be continuously monitored and improved
The ISO 45001 framework goes further. It describes specific parts of an exceptional OHS management system:
- Leadership and Commitment – Senior management must integrate OHS into business operations, allocate resources, and lead by example to create a strong safety culture.
- Worker Participation – Employees play an active role in safety management. Their experience helps identify risks, refine procedures, and improve overall workplace safety.
- Risk-Based Thinking – Organisations must assess risks as well as opportunities to ensure that safety improvements support operational goals.
- Process Approach – Viewing workplace activities as interconnected processes improves efficiency and reduces safety risks across the entire organisation.
- Evidence-Based Decision-Making – Safety strategies should be based on accurate data, such as incident reports, risk assessments, and audit findings.

The PDCA Cycle
There’s no defined endpoint for OHS management under ISO 45001. Instead, the standard adopts the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle of continuous improvement. Broadly speaking, the PDCA cycle involves:
- Plan – Identify OHS risks, set objectives, and establish policies.
- Do – Implement the planned safety measures.
- Check – Monitor and measure OHS performance.
- Act – Enhance OHS management systems based on data and performance reviews.
The cycle is then repeated continually to ensure safety standards remain high and any new risks or developments are accounted for in OHS management.
How is the Standard Structured?
Like other standards, ISO 45001 is structured around ten clauses. (The shared structure makes it easier for businesses to integrate complementary standards.)
The first three clauses are non-auditable, meaning they simply provide context. It’s clauses four through ten that outline implementation requirements. These are:
- Context of the Organisation – Organisations must assess internal and external factors that affect their OHS system, including stakeholder expectations.
- Leadership and Worker Participation – Senior management must take accountability for OHS, establish policies, and ensure workers are involved in safety processes.
- Planning – Organisations must identify OHS risks and opportunities, set objectives, and establish plans to achieve them.
- Support – Businesses must provide the necessary resources, training, communication, and documentation to maintain an effective OHS system.
- Operation – Organisations must implement controls to manage risks, prepare for emergencies, and ensure safe work processes.
- Performance Evaluation – Continuous monitoring, measurement, audits, and reviews must be conducted to assess OHS performance.
- Improvement – Organisations must take corrective actions to address nonconformities and drive continual OHS improvements.

What Are the Benefits of ISO 45001?
The primary benefit of implementing ISO 45001 is safety. The standard provides a structured approach to OHS management, which will help you create a safer workplace.
Organisations that develop robust safety cultures also unlock a range of secondary benefits:
Improved Productivity
Safer workplaces are more productive. Proactively identifying and controlling risks limits the harm they can cause, which saves costs and working hours lost to accidents and incidents.
Employees are also generally more productive when they feel valued and safe at work. Involving your staff in decisions related to their safety and demonstrating a commitment to their wellbeing boosts engagement and retention.
Compliance
Workplace safety is enforced by multiple acts and legal instruments. ISO 45001 accounts for these laws to help businesses ensure compliance. Implementing the standard also demonstrates due diligence in the case of any inspections or post-accident investigations.
Cost Savings
Investing in health and safety saves money.
Accidents have direct costs, such as equipment repairs and potential legal fees or compensation claims. There are indirect costs, too, such as forced downtime, staff absences, and reputational damage.
Keeping workers safe eliminates or reduces these costs. Maintaining an excellent safety record can also lower insurance premiums.
Competitive Advantage and Business Growth
ISO 45001 certification demonstrates a commitment to high safety standards, which can earn credibility with multiple stakeholders. Being known as a safety-conscious employer can also help attract talent and strengthen bids when competing for business.

How Do You Achieve ISO 45001 Certification?
ISO 45001 certification is optional. Businesses can implement the standard without formal certification and still improve workplace safety. However, certification provides external validation that your organisation meets the standard’s requirements.
There are three broad stages to the certification process:
- Implement ISO 45001
- Pass an internal audit before applying for external certification
- Pass an external audit conducted by a recognised certification body
ISO itself doesn’t conduct audits. Certification must be obtained through an accredited third party, and organisations being audited must pay for the service.
Certification isn’t needed to see ISO 45001 benefits. Even without external validation, implementing the standard will help improve safety performance.
How Do You Implement ISO 45001?
Implementing the ISO 45001 framework is possible for any business, regardless of size or sector. But without guidance, gathering the relevant documentation, allocating resources and meeting clauses can seem like a complex and difficult endeavour.
To help you navigate the process, we offer online ISO 45001 Implementation Training. This multi-module course provides the knowledge needed to develop and maintain an OHS management system aligned with ISO 45001:2018. It breaks down the ISO 45001 framework and how to meet each of its key requirements, from initial planning through to implementation and ongoing improvement.
Enrol in ISO 45001 Implementation Training today and learn how you can leverage the standard for a safer, more compliant workplace.