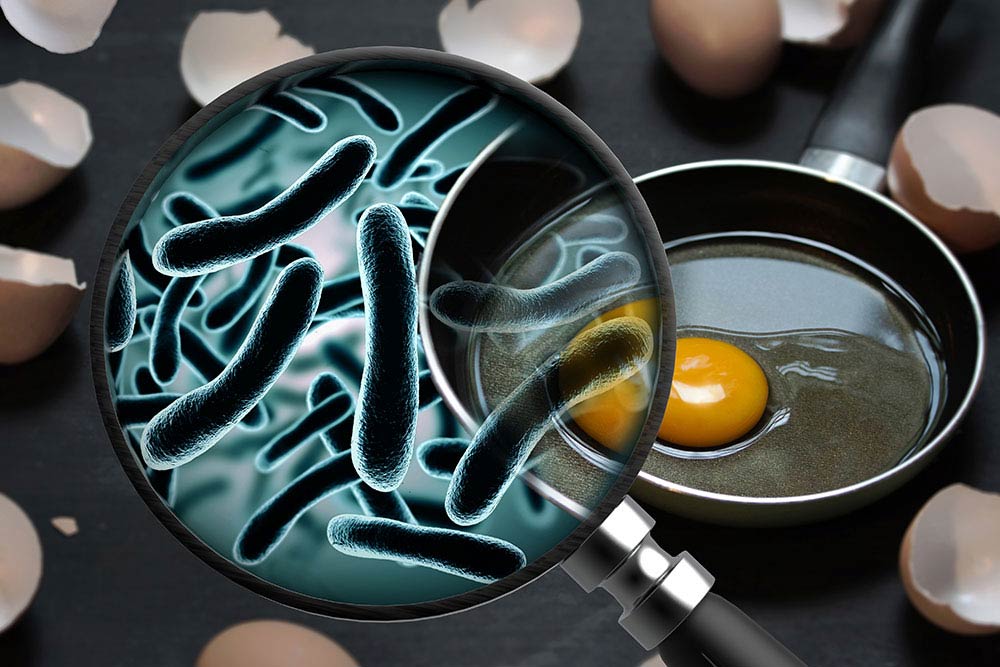
Pest infestations that compromise food safety can damage reputations and ruin food businesses. Effective pest control is crucial to maintain food hygiene standards and comply with legal duties.
In this blog, we’ll explore the most effective strategies for pest control in the food industry and the legal obligations of food businesses in the UK.
Key Takeaways
- Rodents, cockroaches, flies, stored product pests and birds can contaminate food and spread diseases.
- Pest infestations can result in health risks, legal penalties, reputational damage and significant financial losses.
- Food businesses must maintain high standards of hygiene, ensure proper storage, conduct regular inspections and use industry-approved pesticides.
- All employees should be trained to identify pest activity, report infestations and implement effective pest control measures.
Common Pests in the Food Industry
The most common pests in the food sector include:
- Rodents (rats and mice): Known for contaminating food supplies and spreading diseases through droppings and urine.
- Cockroaches: Thrive in warm, moist environments and carry pathogens that can cause foodborne illnesses.
- Flies: Transport bacteria from waste and decaying matter onto food surfaces.
- Stored product pests (beetles, weevils, moths): Infest grains, cereals and other dry food products.
- Birds: Nesting in food facilities can lead to droppings contaminating food and surfaces.
Risks and Consequences of Pest Infestations
Pests such as rodents, insects and birds can contaminate food products, spread diseases and damage infrastructure. A lack of proper pest management can lead to:
- Health hazards: Pests carry harmful pathogens that can lead to foodborne illnesses.
- Regulatory penalties: Non-compliance with food safety laws can result in fines, legal action and facility shutdowns.
- Reputational damage: A single pest-related incident can damage consumer trust and brand reputation.
- Financial Losses: Contaminated food products may lead to recalls, wasted inventory and loss of business.
Best Practices for Pest Control in the Food Industry

1. Integrated Pest Management
Integrated pest management (IPM) is a comprehensive approach that includes the following key components:
- Prevention: Eliminate factors that attract pests, such as food spills and standing water.
- Monitoring: Conduct regular inspections and use traps to detect early signs of infestation.
- Control methods: Utilise chemical, biological and physical pest control techniques as needed.
2. Proper Sanitation and Hygiene
Maintaining cleanliness is one of the most effective ways to prevent pests. To ensure proper sanitation and hygiene, you must:
- Clean food processing areas regularly.
- Ensure proper waste disposal and management.
- Seal food storage containers properly.
- Ensure restrooms and drains are clean and dry.
3. Structural and Physical Barriers
Preventing pest entry requires a well-maintained facility with proper barriers. To ensure this:
- Seal cracks and gaps in walls, floors and doors.
- Install air curtains and screens on entry points.
- Repair leaks to eliminate water sources that attract pests, such as rodents and flies.
4. Pest Monitoring and Surveillance
Early detection helps control pests before they become a major issue. To monitor effectively:
- Implement traps and electronic monitoring systems.
- Conduct routine inspections carried out by trained personnel.
- Keep detailed records of pest activity and control measures.
5. Proper Food Storage Practices
Improper storage can attract pests and lead to infestations. To prevent this:
- Store raw materials and finished products in sealed, pest-proof containers.
- Follow the FIFO (First In, First Out) method to prevent spoilage.
- Keep storage areas dry and well-ventilated.
6. Employee Training and Awareness
Educating employees on pest control measures ensures they actively contribute to a pest-free environment. Training should teach workers how to:
- Identify signs of pest activity.
- Follow proper waste disposal and sanitation protocols.
- Report pest sightings promptly.
7. Use Safe and Approved Pest Control Methods
When pest control treatments are necessary, they should be conducted using industry-approved methods. These include:
- Non-toxic baits and traps.
- Pesticides approved by the Health and Safety Executive and Food Standards Agency.
- Environmentally friendly pest control solutions.
Relevant Legislation and Industry Standards in Great Britain
The following regulations and acts apply to England, Scotland and Wales. Northern Ireland has similar but separate legislation regarding food safety.
1. Food Safety Act 1990
Under the Food Safety Act 1990, food businesses must ensure that food is safe for consumption. Businesses are also accountable for taking appropriate measures to prevent contamination from pests. Under this act, food business operators must:
- Ensure food hygiene and prevent contamination, including pest control.
- Maintain a clean and hygienic environment.
- Conduct inspections and take action if pests are found.
2. The Food Hygiene Regulations 2006
The Food Hygiene Regulations 2006 require food businesses to maintain strict controls to prevent contamination, including measures for pest control. These regulations require businesses to:
- Implement pest management procedures to protect food from contamination.
- Regularly inspect facilities for signs of pest activity and address any infestations immediately.
- Ensure that food preparation and storage areas are maintained to a high level of cleanliness.
- Keep comprehensive records of pest control activities and inspections.
3. The Health and Safety at Work Act 1974
While the Health and Safety at Work Act 1974 primarily focuses on worker safety, it also has implications for food safety. The act mandates employers to take necessary steps to control risks that could harm employees, including pest-related risks in food production facilities. Employers must:
- Provide a safe working environment, which includes pest-free zones for food preparation and storage.
- Ensure appropriate pest control measures are in place to prevent exposure to pests that may transmit diseases.
- Provide proper training to staff on pest control and hygiene procedures to minimise risks.
4. The Control of Pesticides Regulations 1986
The Control of Pesticides Regulations 1986 controls the use of pesticides in food facilities. Under these regulations, food businesses must:
- Use only pesticides approved safe for environments where food is prepared or stored.
- Ensure that pest control chemicals are used following strict guidelines to avoid contamination of food products.
- Maintain proper records of pesticide use.
- Ensure that only certified professionals handle and apply chemicals.
5. British Pest Control Association Standards
The British Pest Control Association (BPCA) sets industry standards for pest control and provides guidelines for pest management in food industries. According to BPCA standards, food businesses should:
- Implement an integrated pest management system.
- Regularly monitor pest activity using traps, surveillance systems and inspections conducted by trained professionals.
- Ensure pest control measures are aligned with best practices for food safety, including regular audits, inspections and the proper use of pesticides.
6. Food Standards Agency Guidelines
Specific guidance on pest control and food safety can also be found in the Food Standards Agency (FSA) guidelines. The FSA provides practical advice to:
- Set up and implement an effective integrated pest management system.
- Regularly monitor food premises for pest activity.
- Ensure food establishments meet hygiene standards in line with the European Union’s Food Hygiene Regulation (EC) No 852/2004.
7. ISO 22000 Food Safety Management System
While ISO 22000 is an international standard, it is widely used in the UK food industry to manage food safety risks, including those associated with pests. To comply with ISO 22000, businesses must:
- Develop a food safety management system that integrates pest control measures.
- Conduct regular risk assessments and develop preventive strategies for pest control.
- Conduct regular audits to ensure that pest control systems are working effectively.
- Provide staff training on pest prevention and control as part of overall food safety practices.
Pest Control and Management Training
Training is vital in preventing infestations before they become costly problems.
Help ensure compliance with food safety regulations and safeguard your business reputation with online Pest Control and Management Training.
The course equips participants with the knowledge to:
- Identify pest activity and potential consequences of infestations.
- Implement effective pest management systems to control and prevent outbreaks.
- Manage ongoing pest prevention and monitoring.
The course will help prevent pest infestation, maintain hygiene and meet regulatory requirements.