Online Manual Handling Training provides a clear, practical introduction to safe manual handling practices in the workplace. It raises awareness of the injury risks linked to lifting, carrying, pushing, and pulling tasks, and outlines the principles of safer manual handling.
Why is Manual Handling Training Important?
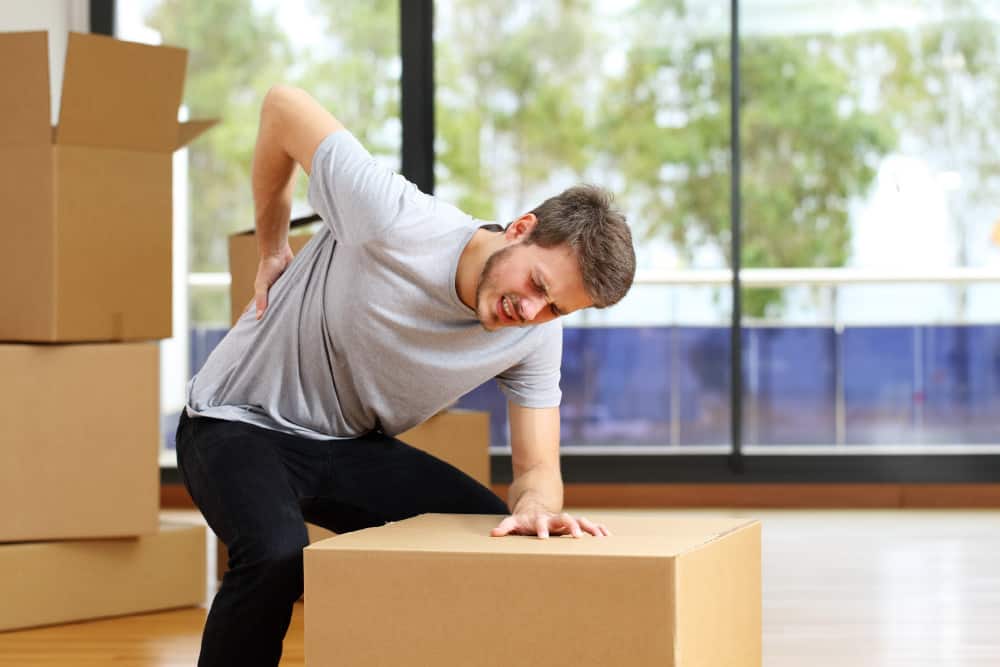
Manual handling involves any task that requires moving or carrying a load by hand or using bodily force, including lifting, lowering, pushing, or pulling. These tasks are so common that workers often underestimate the risk of injury.
In fact, manual handling is the second most common cause of workplace injuries, following only slips, trips, and falls. According to the Health and Safety Executive (HSE), unsafe handling, lifting, and carrying account for 17% of all reported non-fatal workplace injuries.
However, the HSE notes that the actual number of manual handling injuries is likely much higher, as they typically develop over time. These long-term conditions don’t meet the threshold for injury reporting, so they aren’t included in the statistics.
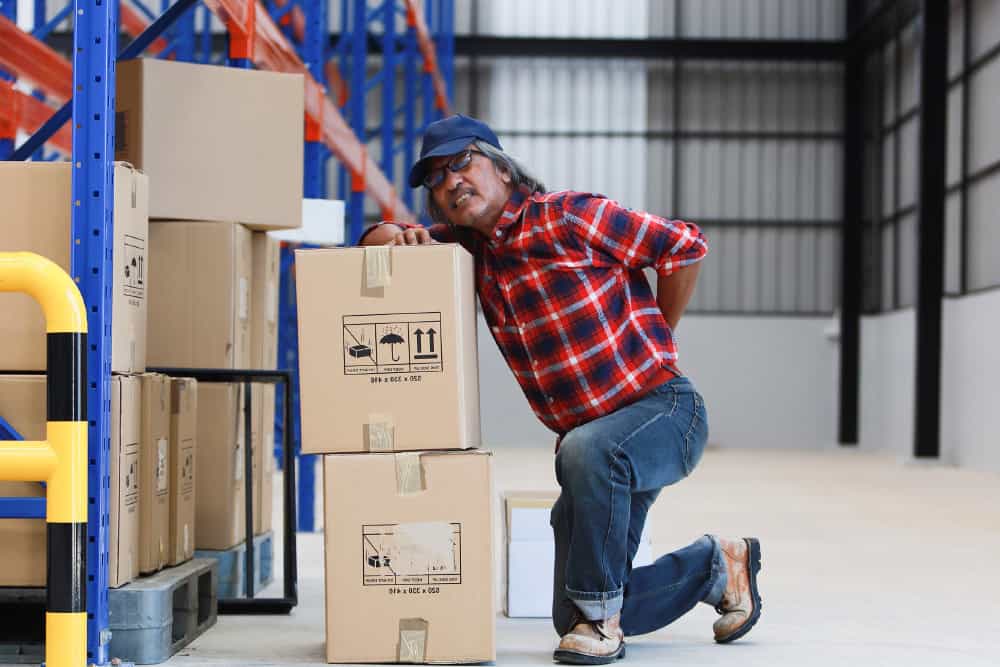
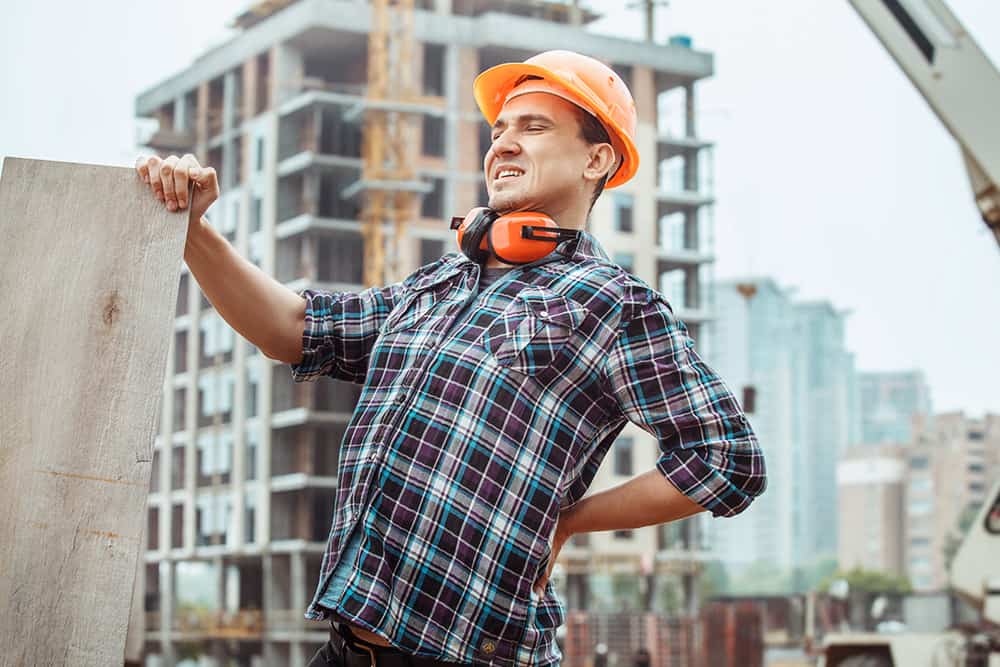
Undertrained workers are at risk of severe, even life-altering musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs), which affect muscles, bones, joints, and connective tissues. MSDs often cause chronic pain and are a leading cause of extended sick leave.
Providing adequate training in manual handling techniques is essential to protect workers from harm and ensure compliance with the Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992. Our manual handling e-learning course equips workers with an awareness of injury risks and safe techniques. Users will understand how to assess tasks and take necessary steps to reduce the risk of injury.
Are You Aware of Your Duties?
Employers have a legal duty under the Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992 to ensure the health and safety of their workers when undertaking manual handling tasks. This duty applies to any work that involves lifting, lowering, pushing, pulling, or carrying loads, whether by hand or with the aid of lifting equipment and machinery.
Employers must ensure the safety and health of their workers by taking the following actions:
- Avoid manual handling operations wherever possible: Employers should eliminate the need to move loads by hand or bodily force wherever practicable.
- Assess risks of manual handling tasks: Employers must undertake appropriate risk assessments of any manual handling that cannot be avoided. This assessment should identify the risks involved and implement control measures to prevent harm.
- Provide adequate information, instruction, and training: Training must make workers aware of the manual handling risks they face and how to manage them.
- Provide suitable work equipment: Employers must provide their workforce with appropriate equipment where it’s necessary to reduce injury risks. Examples include lifting aids or personal protective equipment.
- Monitor and review: Employers must monitor manual handling activities and regularly review risk assessments to ensure their ongoing effectiveness.
Employers who neglect their health and safety duties risk legal action, including enforcement notices and fines.
This course helps workers minimise manual handling injury risks and supports legal compliance with the Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992.
Who Needs This Course?
This Manual Handling Training course is designed for individuals across a wide range of sectors where lifting, carrying, pushing, or pulling is a routine part of the job, including:
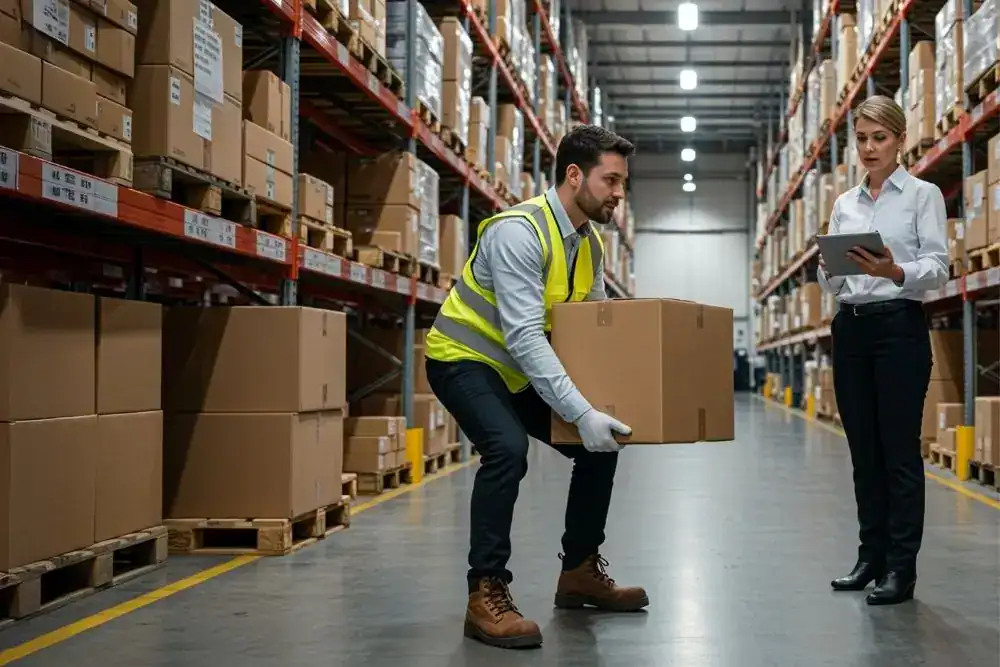
- Warehouse workers – who are responsible for picking, packing, loading and unloading goods.
- Construction workers – who handle building equipment, materials and tools on-site.
- Office workers – who lift and move office equipment, furniture, or supplies.
- Retail workers – who stock shelves, manage deliveries and move displays.
- Factory workers – who handle materials on production lines, in storage areas or during dispatch.
- Agricultural workers – who move tools, equipment, animal feed, or produce.
This course helps all staff in physically active roles understand how to assess manual handling risks, apply safe techniques, and take proactive steps to avoid injury. It provides foundational awareness for anyone involved in manual handling tasks, no matter the industry.
Key Benefits
Understanding the principles of safe manual handling helps prevent injuries caused by lifting, carrying, pushing, or pulling tasks. From a business perspective, this can lower costs related to absences, sick pay, and lost productivity. Promoting awareness of manual handling risks also supports a safer working culture and helps meet regulatory expectations.
Here is how Manual Handling Training can benefit your organisation:
- Better handling awareness: Trainees will learn to identify manual handling risks and apply safe techniques in routine tasks.
- Stronger legal compliance: The course supports the employer’s duty to provide training under the Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992.
- Lower absence and injury costs: Improved awareness can reduce the risk of musculoskeletal disorders that lead to long-term sick leave.
- Faster onboarding: New employees can receive essential handling awareness training as part of their induction.
- Consistent training across roles and sites: Suitable for a wide range of sectors and job functions, from warehouse and construction to office and retail environments.